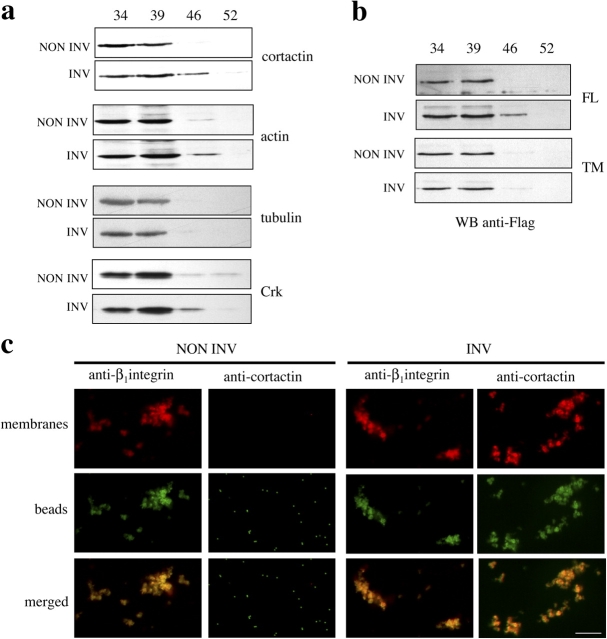
Figure 4.
Shigella invasion induces cortactin association with plasma membranes. After challenge with noninvasive (NON INV) or invasive (INV) Shigella, cell extracts were fractionated using a discontinuous sucrose gradient. (a) Extracts from HeLa cells were fractionated and analyzed by anti-cortactin, anti-actin, anti-tubulin, and anti-Crk Western blot. Invasive Shigella induces a shift of cortactin to the plasma membrane–containing fraction. Actin and Crk co-shift with cortactin, but not with tubulin. (b) Extracts from cells transfected with full-length (FL) or tyrosine-mutated cortactin (TM) were fractionated and analyzed by anti-Flag Western blot. (c) Cells were surface labeled with a rhodamine derivative (red) previous to bacterial invasion. After cell extract fractionation on sucrose gradients, the plasma membrane–enriched 46% sucrose fraction was incubated with FITC-fluorescent beads (green) coupled to anti-cortactin or anti-β1 integrin antibodies. Beads were recovered by centrifugation and fluorescence analysis was performed to determine the presence of plasma membranes. Bar, 5 μm.