Figure 1.
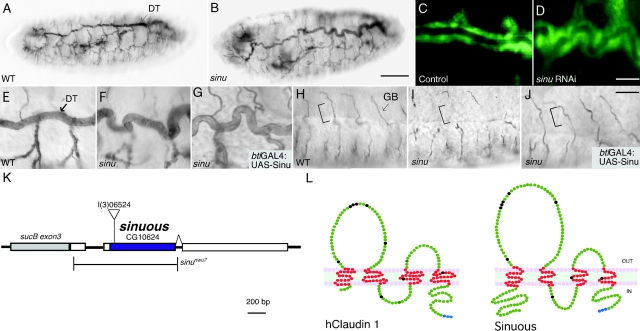
Sinuous encodes a claudin family member required for tracheal tube size control. (A–G) The multicellular tracheal dorsal trunks (DT) in sinuous mutants (B and F) have trachea that are too long and have some diameter expansions compared with wild-type (WT) animals (A and E). (H–J) sinuous mutants (I) also have missing lumenal segments in their ganglionic branches (GB), where tubes are formed by single cells with autocellular junctions (square brackets). (C and D) Injection of double-stranded RNA corresponding to CG10624 into btl-GAL4:UAS-GFP embryos causes the same phenotypes as sinuous mutants (D), whereas buffer-injected control embryos have normal trachea (C). Expression of the CG10624 ORF in sinuous homozygotes using the btl-GAL4 tracheal driver and a UAS-Sinuous responder rescues the ganglionic branch defects (J), but not the dorsal trunk length defects (G). btl-GAL4 driven expression of Sinuous in the tracheal system in an otherwise WT background did not cause any apparent defects (not depicted). (K) A schematic representation of the sinuous locus. The sinuous l(3)06524 strain contains a transposable element insertion at the beginning of the CG10624 ORF. sinu nwu7 is a null mutation that deletes all the amino acids of the sinuous ORF without affecting the coding sequences of adjacent genes. (L) Sinuous is predicted to encode a 247-aa protein with four transmembrane domains and a topology similar to vertebrate claudins. hClaudin-1 is shown as a representative vertebrate claudin. Conserved claudin residues present in Sinuous and hClaudin-1 are shown in black, and the putative PDZ-binding domain residues are blue (see Results for details). Predicted transmembrane domain residues are red. All embryos stage 16; A, B, and E–J stained with the anti-lumenal 2A12 mAb. Genotypes: wild-type, Oregon-R; sinu nwu7; sinuous rescue, blt-GAL4 UAS-Sinuous; sinu nwu7. Bars: B, 50 μm (for A and B); D, 10 μm (for C and D); J, 10 μm (for E–J).