Figure 3.
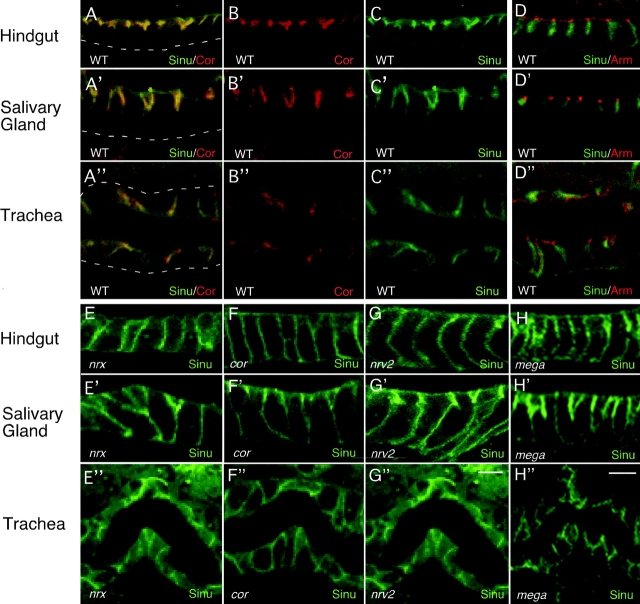
Sinuous localizes to septate junctions in wild-type animals, but not in most septate junction mutants. In wild-type embryos stained with anti-Sinuous (A and C, green) and anti-Cor (A and B, red) antibodies, Sinuous colocalizes almost entirely with Cor at septate junctions in the hindgut, salivary gland, and trachea (A–A′′). (D) Sinuous (green) does not localize to the adherens junctions, marked by Arm (D–D”; red). (E–H) Sinuous localization to septate junctions depends on Cor, Nrx, Mega, and Nrv2 as Sinuous is mislocalized and/or reduced in animals homozygous for null mutations in these genes (E–H”). In the partial loss-of-function mega VE896 mutants, the localization and levels of Sinuous are reduced in the hindgut and trachea, but appear normal in the salivary glands (not depicted). All images of stage 16 animals. Dashed lines mark basal cell surfaces. Genotypes: WT, sinu/+; nrx 486 5; cor5; nrv223B; sinu nwu7; megaG0044. Bar in G and H (represents all panels), 5 μm.