Figure 6.
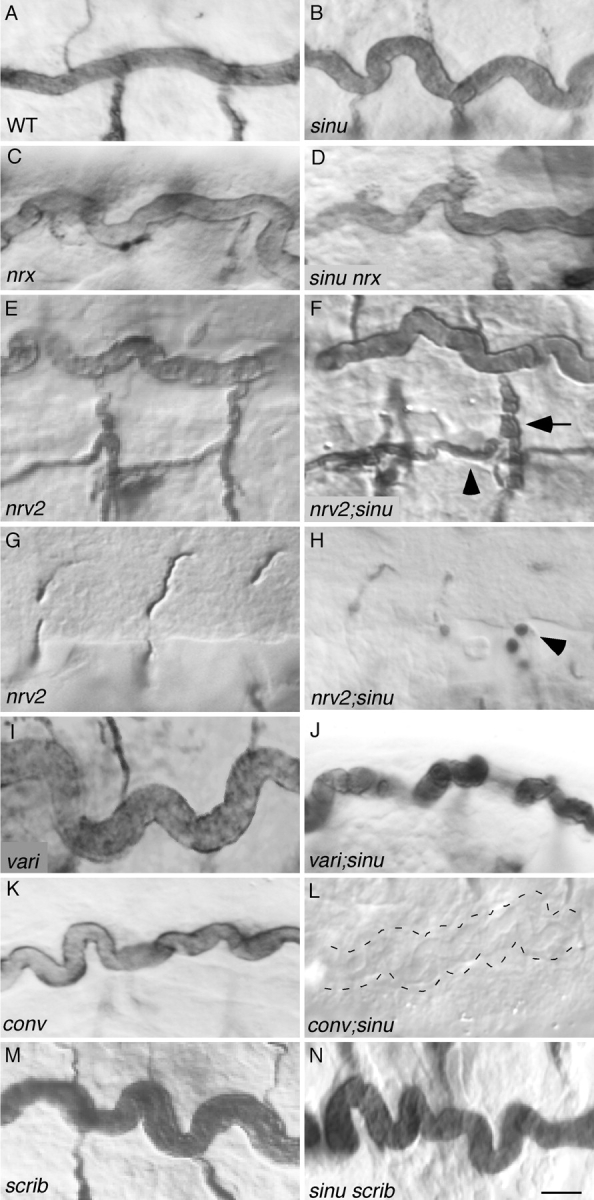
Sinuous acts in one branch of a tube size control pathway. sinu nrx (D) and sinu scrib (N) double mutants have the same phenotype as sinu single mutants (B), suggesting that scrib and nrx act in the same genetic pathway as sinuous. In contrast, double mutant combinations of a sinuous null mutation with nrv2, conv or vari, mutations (F, H, J, and L) all cause tracheal phenotypes that are more severe than the sinuous null mutation (B), suggesting that these genes act in a genetic pathway(s) or branch of a pathway(s) that sinuous does not act in. nrv2;sinu double mutants have somewhat more severe diameter expansions in the transverse connective and visceral branches (F, arrow and arrowhead, respectively) and have cyst-like structures (H, arrowhead) in their ganglionic branches compared with sinuous or nrv2 null mutants (compare Fig. 6 H to Fig. 1 I). conv;sinu double mutants have greatly increased length and diameter defects in all multicellular branches, and the dorsal trunk fails to stain with the lumenal antigen 2A12 by mid-stage 16 (L, dotted lines outline the dorsal trunk). Genotypes: WT, Oregon-R; sinu nwu7; nrx 4865; nrv2, nrv2 23B in E, nrv2 nwu3 in G; conv l(2)k06507; var il(2)03953; scrib, scrib 2/scribj7B3 in M, scrib 2 in N. Bar in N (represents all panels), 5 μm.
