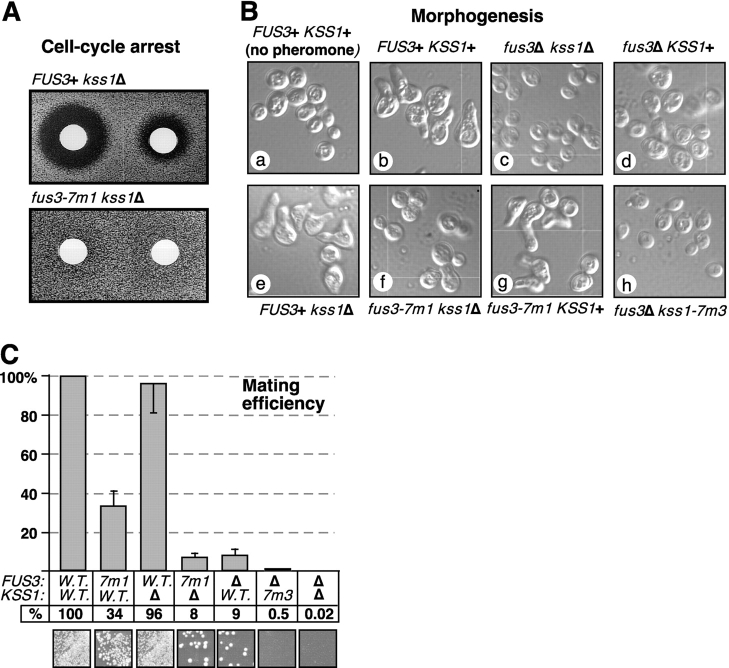
Figure 5.
The CD/7m MAPK mutants have multiple defects in the mating pheromone response. Strains were generated as in Fig. 4. (A) Pheromone-imposed cell-cycle arrest. A lawn of cells was grown for 48 h in the presence of disks containing 12 μg (left) or 3 μg (right) of α-factor mating pheromone. Pheromone-imposed cell-cycle arrest is indicated by the zone of growth inhibition (“halo”) surrounding a disk. (B) Pheromone-induced morphogenesis. Cells were treated for 4 h with 5 μM α-factor, fixed, and photographed at a magnification using a microscope and imaging system. (C) Mating. The strains analyzed in B were scored for mating to a tester strain (DC17) using a quantitative assay. Mating efficiencies (diploids formed per input MATa haploid) are normalized to the value (0.13) obtained for cells expressing wild-type Fus3 and Kss1. Each experiment was repeated three to six times; error bars are shown. The photos at the bottom show the results of a qualitative mating assay performed in parallel.