Figure 4.
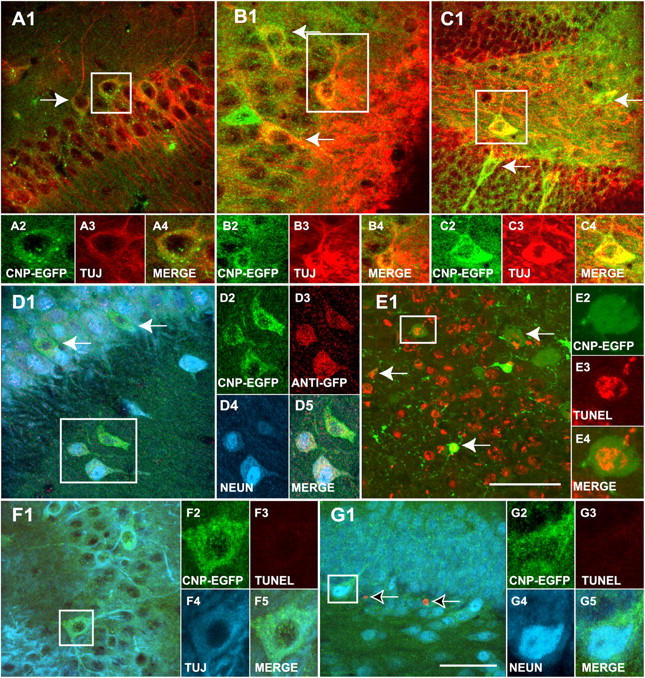
Grafted NG2 + /EGFP + cells differentiate to neurons in the hippocampus. (A–C) 3 wk after transplantation, all the grafted EGFP+ cells (green) in the hippocampus are labeled with TUJ1 (red) antibodies. EGFP+/TUJ1+ cells (green/red, respectively) are found in the pyramidal layer of the CA1 (A1) and CA3 (B1). Grafted cells are also found in the hilar region of the DG (C1). (D) A large percentage of transplanted EGFP+ cells (green) are also labeled with anti-NeuN (blue) antibodies in the CA3 area and hilar region of the DG (not depicted), confirming the neural fate of the grafted NG2+/EGFP+ cells. The tissue was also stained with anti-GFP antibodies (D3, red), confirming that these neurons are derived from the transplanted NG2+/EGFP+ fraction. (E–G) Neurons derived from grafted NG2+/EGFP+ cells are viable, as determined by TUNEL assay. (E) Positive control (Dnase I-treated tissue). EGFP+/TUJ1+ (F, green/blue, respectively) and EGFP+/NeuN+ (G, green/blue, respectively) grafted cells are TUNEL-negative (red) 6 wk after transplantation. Arrows in A1–D1 indicate EGFP+ neurons derived from grafted cells. Arrows in E1 indicate EGFP+/TUNEL+ cells after DNAse treatment of the tissue (positive control). Arrows in G1 indicate endogenous EGFP-negative TUNEL+ cells in DG. EGFP+ cells in boxed areas are shown at higher magnification. Bars: (A–D , F, and G) 50 μm; (E) 100 μm.
