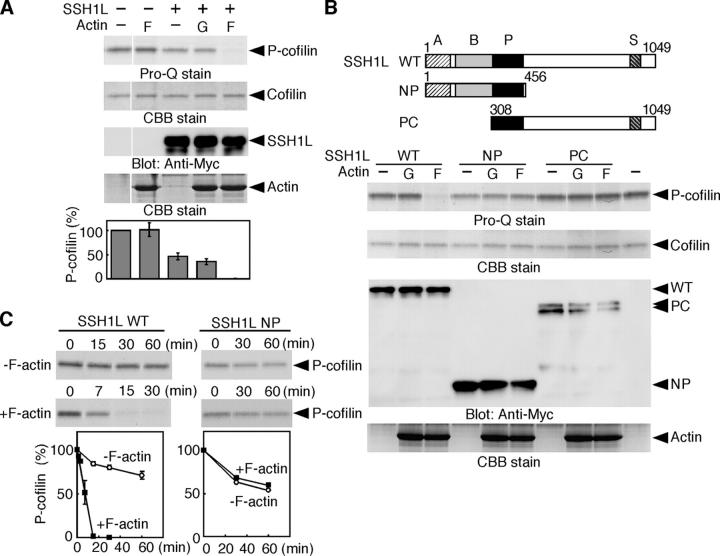
Figure 2.
F-actin activates the cofilin-phosphatase activity of SSH1L. (A) F-actin activates SSH1L. Myc-SSH1L expressed in COS cells was precipitated with anti-Myc antibody and subjected to in vitro phosphatase assay, using cofilin-(His)6 as a substrate, with or without F-actin (F) or G-actin (G). P-cofilin and total cofilin were measured by Pro-Q and Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining, respectively. The bottom panel indicates the P-cofilin levels, as means ± SD of triplicate experiments. (B) F-actin activates SSH1L(WT), but not its NP or PC fragment. The conserved regions between a SSH family are indicated as A, B, P (phosphatase), and S domains. Cofilin-phosphatase activities of Myc-SSH1L(WT) and its NP and PC fragments with or without F- or G-actin were analyzed as in A. (C) Kinetic analyses of cofilin-phosphatase activity of WT and NP mutant of SSH1L with or without F-actin. Top panels show the P-cofilin levels at indicated times after incubation with WT or NP mutant of SSH1L, measured by Pro-Q staining. Bottom panels indicate the time courses of P-cofilin dephosphorylation as means ± SD of triplicate experiments.