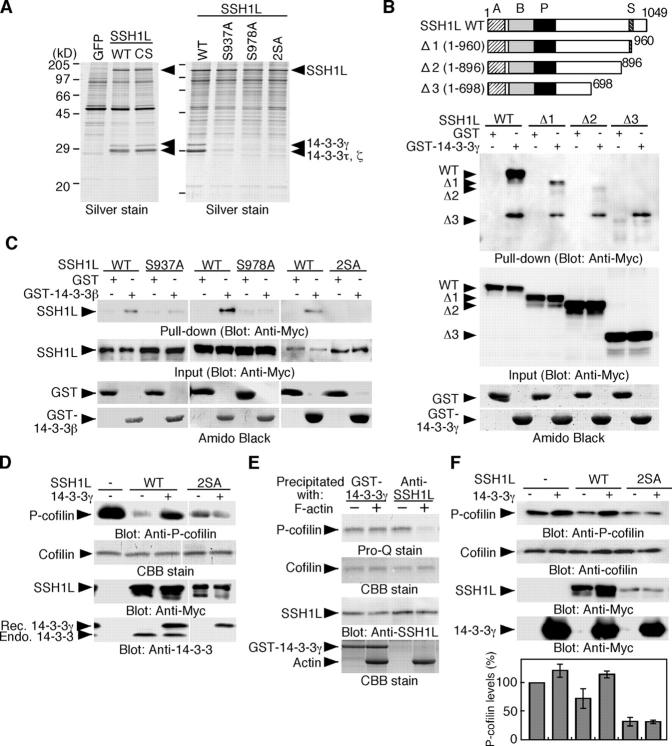
Figure 3.
14-3-3 proteins bind to and inhibit SSH1L, dependent on Ser-937 and Ser-978 phosphorylation. (A) Purification of 14-3-3 proteins as SSH1L-interacting proteins. Lysates of COS cells expressing WT or CS mutant of (Myc+His)-SSH1L were precipitated with Ni-NTA agarose, run on SDS-PAGE, and stained by silver. Right panel shows similar experiments done for the indicated mutants of (Myc+His)-SSH1L. (B) The COOH-terminal region of SSH1L is required for binding to 14-3-3β. WT and deletion mutants of Myc-SSH1L were expressed in COS cells and subjected to in vitro pull-down assay with GST or GST-14-3-3β. (C) SSH1L interacts with 14-3-3β, dependent on Ser-937 and Ser-978 phosphorylation. WT and point mutants of Myc-SSH1L expressed in COS cells were subjected to in vitro pull-down assay. (D) 14-3-3γ inhibits SSH1L, but not its 2SA mutant, in cell-free assay. Myc-SSH1L or its 2SA mutant expressed in 293T cells were precipitated with an anti-Myc antibody and subjected to in vitro phosphatase assay, using cofilin-(His)6 as a substrate, with or without recombinant (Rec.) 14-3-3γ. Reaction mixtures were analyzed by blotting with anti–P-cofilin antibody. It is noted that SSH1L(WT), but not its 2SA mutant, coprecipitated endogenous (Endo.) 14-3-3 proteins (bottom). (E) 14-3-3γ protects SSH1L from F-actin– induced activation. Endogenous SSH1L in MCF-7 cells was precipitated with anti-SSH1L antibody or GST-14-3-3γ and subjected to in vitro phosphatase assay, as in Fig. 2 A. (F) Expression of 14-3-3γ increases the cellular P-cofilin level and suppresses SSH1L-induced cofilin dephosphorylation. Myc-14-3-3γ was expressed alone or with WT or 2SA mutant of Myc-SSH1L in COS cells, and lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. The bottom panel indicates the relative levels of P-cofilin as means ± SD of triplicate experiments.