Figure 2.
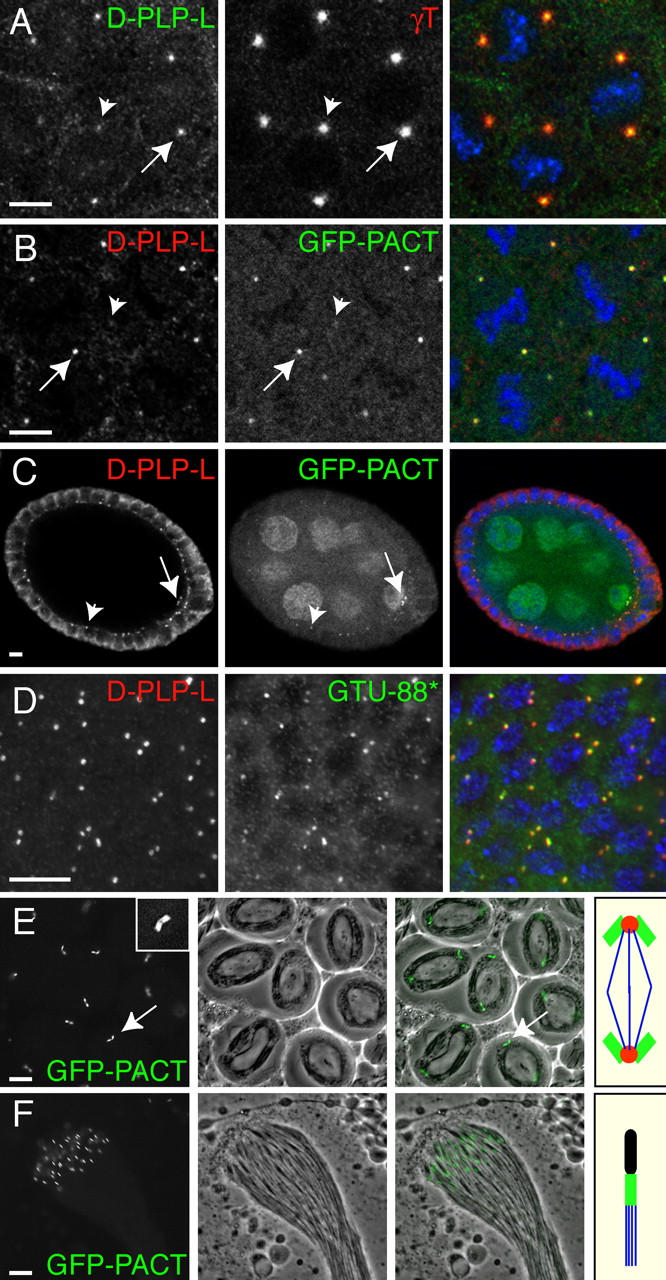
D-PLP and GFP-PACT are associated with centrioles. (A) In fixed WT embryos, anti-D-PLP-L antibodies stain centrosomes as a small dot that is located in the center of the PCM (stained here with anti-γ-tubulin antibodies). (B) GFP-PACT colocalizes with D-PLP in these small dots. Note that the intensity of the D-PLP and GFP-PACT staining varies from centrosome to centrosome (A and B, arrows and arrowheads). This is because the D-PLP and GFP-PACT dots are so small that they often cannot all be visualized in the same optical section. (C) In Drosophila oocytes, D-PLP and GFP-PACT colocalize in small dots that appear to be the centrioles (arrows; see text). Both markers also stain the centrioles in the follicle cells that surround the oocyte and nurse cells (arrowheads). GFP-PACT is also present in the oocyte and nurse cell cytoplasm and nuclei, presumably because this fusion protein is expressed at higher levels than the endogenous protein. (D) GTU88* and anti-D-PLP-L antibodies recognize the centrioles in interphase larval neuroblasts. In A–D, DNA is shown in blue in the merged images. (E) In living WT spermatocytes, GFP-PACT is concentrated in the large pair of orthogonally arranged centrioles at the poles of each meiosis I spindle (arrow; inset shows a 3×-magnified view of a centriole pair). The middle panel shows a phase-contrast image, and the right panel a merged image. The panel on the far right shows a schematic representation of the centrioles (green), PCM (red), and microtubules (blue) in a typical meiosis I spindle. (F) In a WT cyst of maturing sperm, GFP-PACT is concentrated in the centrioles/basal bodies located at the base of each sperm flagellum. The panel on the far right shows a schematic representation of the DNA (black), centriole/basal body (green), and microtubules (blue) in a single sperm. Bars, 10 μm.
