Figure 6.
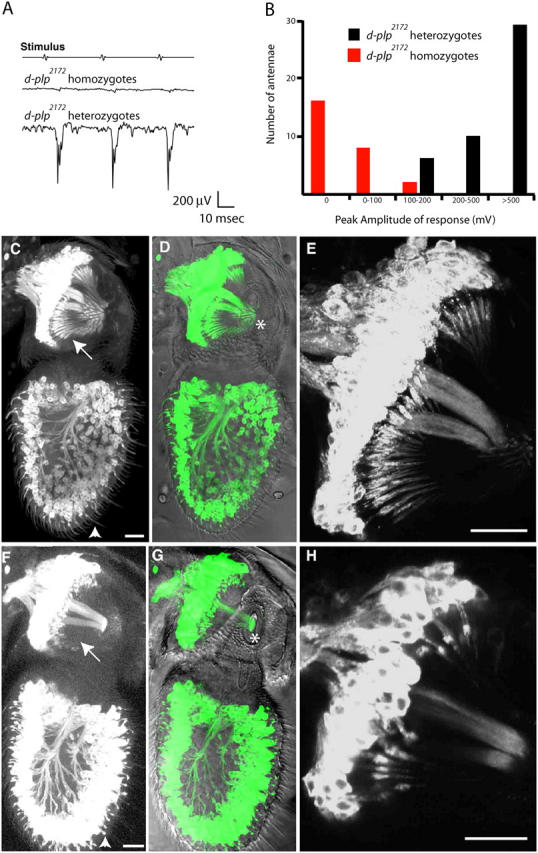
d-plp2172 mutants have defects in mechanosensory neuron function. (A) A trace of the SEPs originating from the auditory chordotonal organ of a d-plp 2172 homozygous and a d-plp 2172 heterozygous adult. (B) The distribution of the peak SEP amplitudes in d-plp 2172 homozygotes (red) and d-plp 2172 heterozygotes (black). (C–H) Micrographs show the chordotonal neurons in the second and third antennal segments of WT flies (C–E) or d-plp 2172 homozygous mutant flies (F–H). The neurons express the mCD8-GFP membrane marker (left panel; green in image merged with a DIC view); a magnified view or the second segment is shown in E and H. In d-plp 2172 heterozygous antennae, the extended outer segment cilia of the mechanosensory chordotonal neurons in the second antennal segment (arrows) and the chemosensory neurons in the third antennal segment (arrowheads) are clearly visible. In d-plp 2172 homozygous mutant antennae, most of these extended cilia are either absent or short and kinked, and the chordotonal cilia of the second segment fail to attach to the cuticle that connects the second and third antennal segments (asterisk). Bars, 20 μm.
