Figure 1.
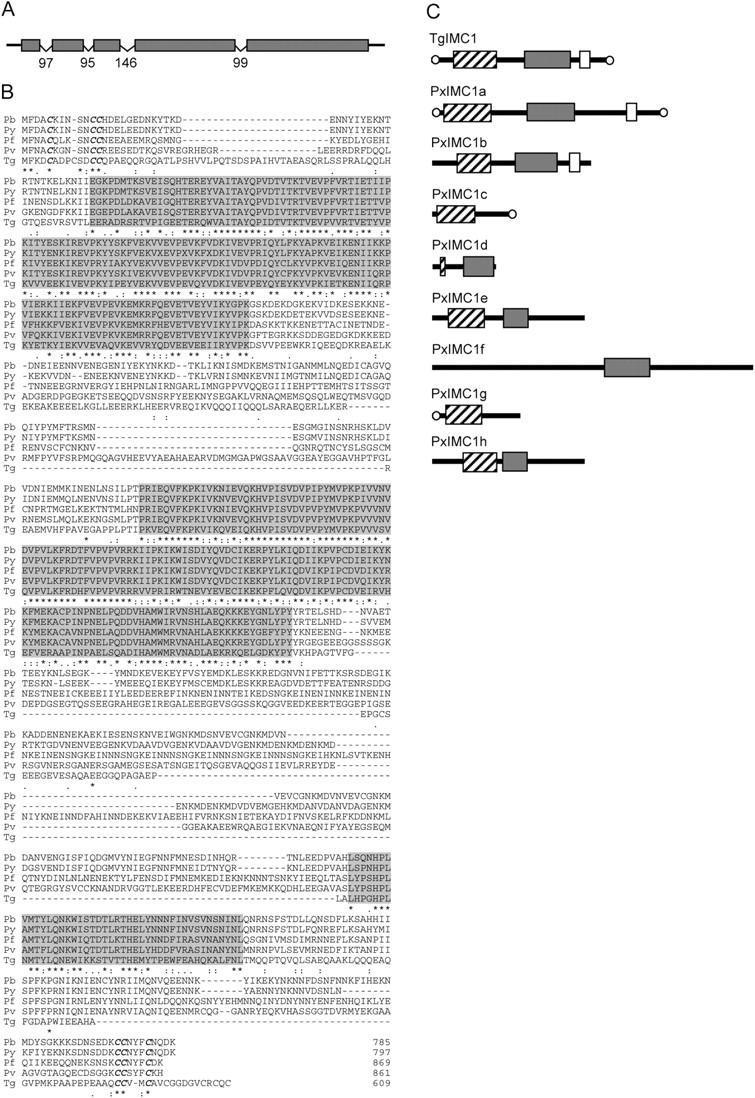
Sequence and structure of PbIMC1a. (A) Diagram of the intron/exon structure of the PbIMC1a gene. Introns are indicated with v-shaped lines with sizes in nucleotides. (B) ClustalW multiple alignment of PbIMC1a (Pb), PyIMC1a (Py), PfIMC1a (Pf), PvIMC1a (Pv), and TgIMC1 (Tg). Indicated are conserved domains (shaded); terminal cysteine motifs (bold and in italics); gaps introduced to allow optimal alignment (hyphens). Conserved amino acid identities (asterisks) and similarities (colons and points) are shown underneath. (C) Schematic diagram of the protein structure of TgIMC1 and its structural homologues in Plasmodium spp. The proteins shown are based on predicted proteins of P. yoelii, GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession nos. EAA16469 (PyIMC1a), EAA15257 (PyIMC1b), EAA16185 (PyIMC1c), EAA17029 (PyIMC1d), EAA15249 (PyIMC1e), EAA15609 (PyIMC1f), EAA15402 (PyIMC1g), and EAA20426 (PyIMC1h). Boxes mark domains corresponding to the conserved amino-terminal domain (hatched), central domain (gray), and carboxy-terminal domain (open). Conserved terminal cysteine motifs are indicated with open circles.
