Figure 1.
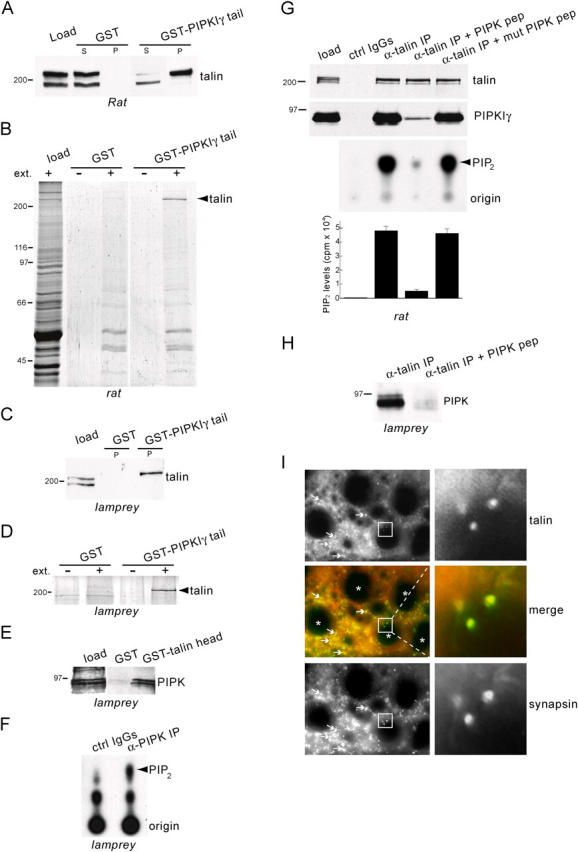
Interaction of PIPK with talin and synaptic localization of talin in the lamprey spinal cord. (A) Western blot with an anti-talin antibody of rat brain extract (load) and the material affinity purified from such extract by either GST or GST-PIPKIγ tail in pull-down experiments (S, supernatant; P, pellet). The top talin band is pulled down selectively by GST-PIPKIγ tail. (B) Coomassie blue–stained protein gel of a pull-down with GST-PIPKIγ tail from rat brain extracts (ext.) showing specificity of the talin–PIPKIγ interaction. (C) Western blot with an anti-talin antibody of lamprey extract (load) and of the material purified by either GST or GST-PIPKIγ tail. (D) Coomassie blue–stained protein gel of a pull-down with GST-PIPKIγ tail from lamprey spinal cord extracts. (E) Western blot with an anti-PIPKIγ antibody of lamprey extract (load) and of the material purified by either GST or GST-talin head. The 90-kD doublet is specifically affinity purified by GST-talin head. (F) TLC demonstrating the generation of phosphoinositides from lamprey extracts by immunoprecipitates of PIPKIγ antibody (α-PIPK IP) or control IgGs (ctrl IgGs). Note the prominent [32P]PIP2 band produced by the α-PIPK IP. (G, top panels) Western blots of anti-talin immunoprecipitates from rat brain extracts showing that coprecipitation of PIPKIγ (“α-talin IP” lane) is prevented by PIPK pep but not mutant PIPK pep (100 μM). (G, bottom panels) TLC and quantification of [32P]PIP2 showing correlation between PIPKIγ coprecipitation and PIP2-synthesizing activity. (cpm, counts per minute). (H) Western blot of anti-talin immunoprecipitates from lamprey spinal cord extracts showing that the PIPK pep (300 μM) prevents coprecipitation of PIPK. (I) Double immunofluorescence of cross sections of lamprey spinal cord stained for talin (red) and for the presynaptic marker, synapsin (green). Arrows indicate synapses in the neuropil. Asterisks indicate reticulospinal axons. Note the colocalization of talin with synapsin at the reticulospinal synapses (insets).
