Figure 3.
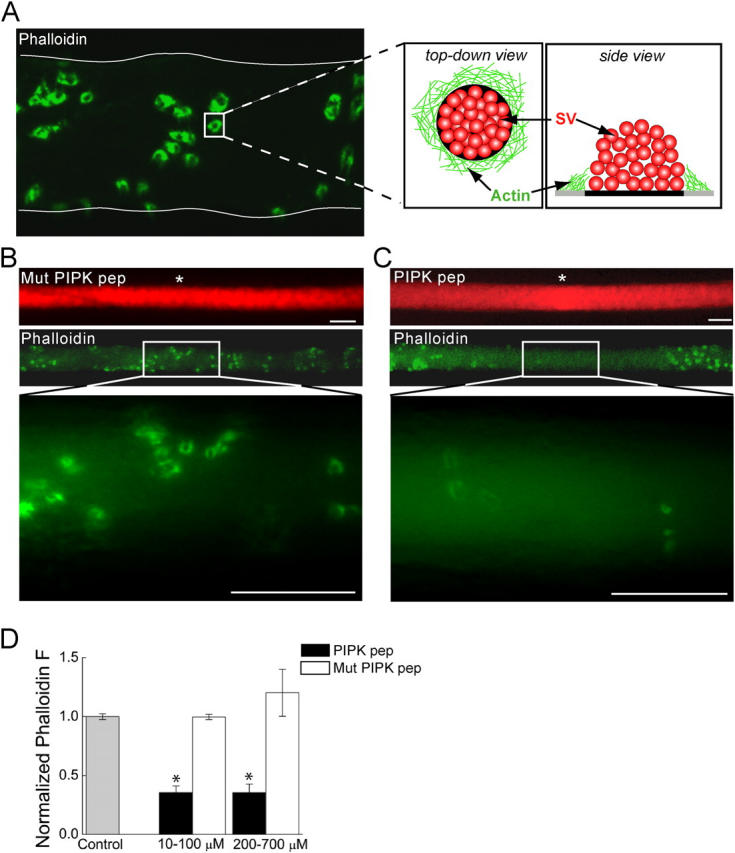
Microinjection of PIPK pep disrupts the actin cytoskeleton at synapses. (A) Confocal image of a lamprey reticulospinal axon injected with Alexa 488–phalloidin (green). Thin, white line denotes axonal border. Phalloidin labels rings of actin at periactive zones of synapses, as indicated by the cartoon (SV, synaptic vesicle). (B and C) Images of axons injected with rhodamine-conjugated (red) Mut PIPK pep or PIPK pep and then with Alexa 488–phalloidin at sites indicated by white asterisks. Although Mut PIPK pep had no effect (B), the fluorescence intensity of phalloidin rings is greatly diminished by PIPK pep (C). Bars, 20 μm. (D) Average fluorescence intensity of the phalloidin rings over several concentration ranges of PIPK peptides as compared with that in the absence of any peptides (Control). Data indicate mean values and SEM from synapses in 31 control, 15 PIPK pep–injected, and 14 Mut PIPK pep–injected axons. Asterisks indicate statistical significance as compared with control (for PIPK pep 10–100 μM, P < 0.05 × 10−13; for PIPK pep 200–700 μM, P < 0.05 × 10−8; t test).
