Figure 4.
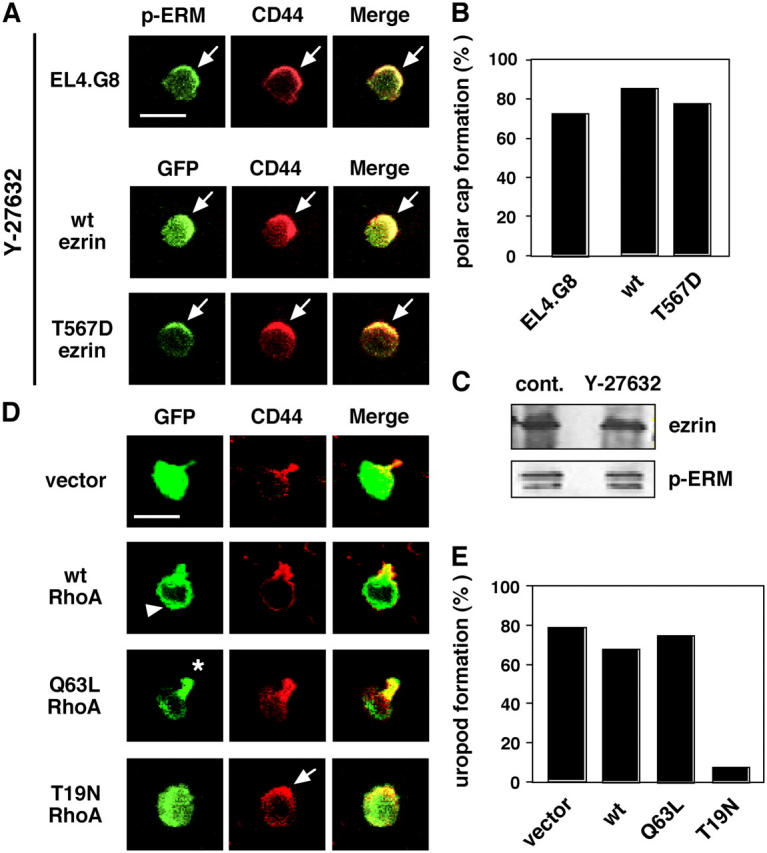
The Rho–ROCK pathway is involved in uropod formation. (A) Y-27632 abolishes uropod but not polar cap formation (arrows). Y-27632–treated parental EL4.G8 cells were stained for p-ERM and CD44 (top panels). GFP-tagged WT and T567D ezrin were also colocalized with CD44 in Y-27632–treated stable transfectants (middle and bottom panels). Bar, 10 μm. (B) Percentage of cells exhibiting the polar cap in A (n > 150). (C) Y-27632 does not alter the phosphorylation status of ERM proteins. The total amount of ezrin and the p-ERM level were determined by Western blotting using lysates from control or Y-27632–treated EL4.G8 cells. (D) WT RhoA shows a diffuse distribution in the cytoplasm, including the leading edge (arrowhead). Constitutively active (Q63L) RhoA is preferentially localized at the rear part of the cells (asterisk), and a dominant-negative form (T19N) abolishes uropod formation but not polar cap formation (arrow). EL4.G8 cells were transiently transfected with WT, Q63L, or T19N RhoA and examined for GFP and CD44 24 h after the transfection. Bar, 10 μm. (E) Percentage of cells exhibiting the uropod in D (n > 75).
