Figure 6.
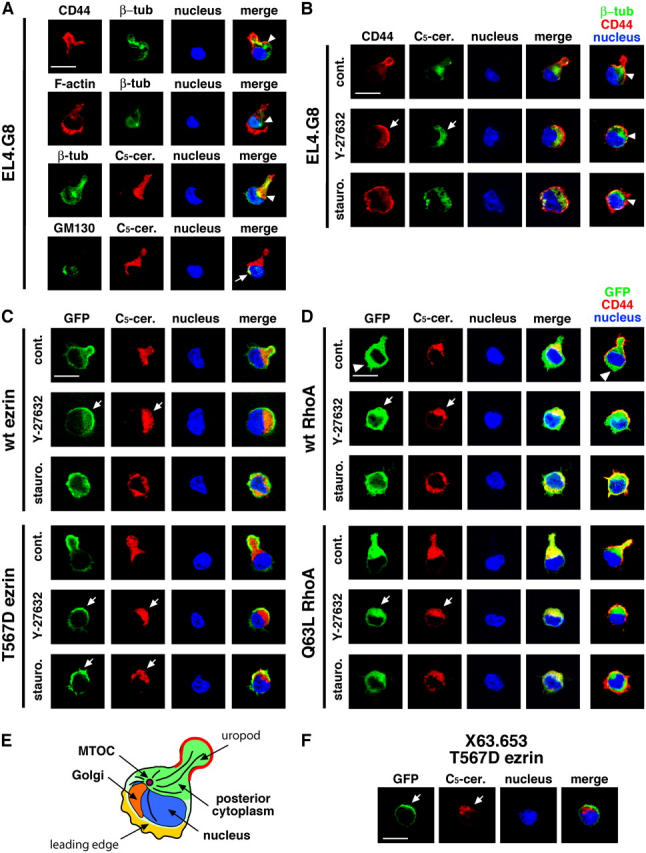
A polar cap covers the posterior part of the cell. (A) EL4.G8 cells exhibit a unique cytoplasmic polarity. EL4.G8 cells were stained for CD44 and β-tubulin, F-actin and β-tubulin, β-tubulin and the posterior cytoplasm (C5-ceramide), or GM130 and the posterior cytoplasm (C5-ceramide). Arrowheads and an arrow indicate the positions of the MTOC and the Golgi apparatus, respectively, in each cell. (B) The polar cap is constructed over the posterior part of the cytoplasm (arrows). Y-27632– or staurosporine-treated EL4.G8 cells were stained for CD44 and the posterior cytoplasm. Composite images for β-tubulin/CD44/nucleus are shown (right) together with the MTOC position (arrowheads). (C) The T567D ezrin–associated polar cap covers the posterior cytoplasm in Y-27632– or staurosporine-treated transfectants (arrows). A similar situation is observed in Y-27632 but not in staurosporine treatment in WT ezrin transfectants (arrows). (D) WT and Q63L RhoA show different intracellular localization in the stable transfectants. WT RhoA is distributed diffusely in the cytoplasm, including the leading edge (arrowheads), whereas Q63L RhoA is localized in the posterior cytoplasm beneath the uropod, or beneath the polar cap when the transfectant is treated with Y-27632 (arrows). Similar but less clear localization of WT RhoA in the posterior cytoplasm is also observed in Y-27632-treated WT RhoA transfectants (arrows). (E) Schematic representation of a typical arrangement of cellular structures in an EL4.G8 cell. (F) The T567D ezrin–associated polar cap covers the posterior cytoplasm in X63.653 cells (arrows). Bars (A–D and F), 10 μm.
