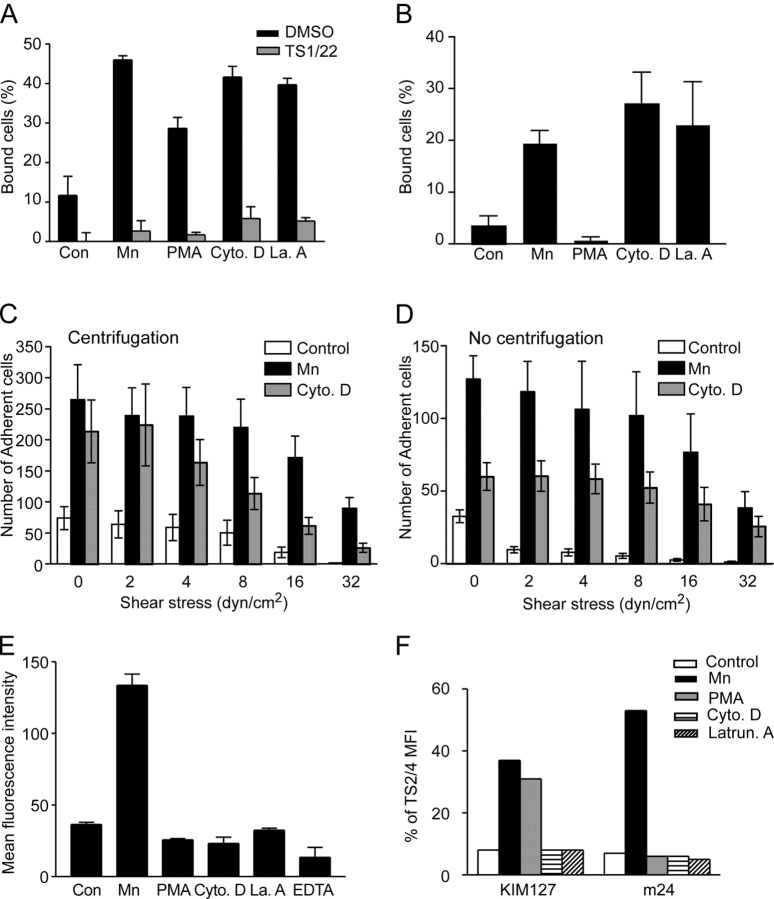
Figure 3.
Disruption of cytoskeletal constraints enhances cell adhesion but does not promote soluble ligand binding or conformational change. (A and B) K562 transfectants expressing wild-type αLβ2 were preincubated with Mn2+, PMA, cytochalasin D, or latrunculin A in the absence or presence of inhibitory αL mAb TS1/22 (10 μg/ml) and allowed to bind ICAM-1 immobilized on V-bottom (A) or flat-bottom (B) plates, as described in Materials and methods. Data represent mean ± SEM of all measurements from three independent experiments in duplicate (A) or three independent experiments in triplicate (B). (C and D) Stable K562 cell transfectants expressing wild-type αLβ2 were allowed to adhere, with (C) and without (D) an initial centrifugation, to coverslips coated with ICAM-1 in the absence (Control) or presence of 1 mM Mn2+ or 1 μM cytochalasin D for 30 min at 37°C under static conditions. Coverslips were transferred to a laminar flow chamber and cells were then detached by a shear regimen of 30 s each of 0, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 dyn/cm2. The number of cells remaining after each interval were counted. Values are mean ± SEM for three separate experiments. (E) Binding of soluble, multimeric ICAM-1-Fcα chimera/anti-IgA-FITC complex was conducted in the presence of Mn2+, PMA, cytochalasin D, or latrunculin A at 37°C and measured by flow cytometry. Data show mean ± SEM of three experiments, each in triplicate. (F) Binding of conformation-sensitive antibodies KIM127 and m24 in the absence or presence of Mn2+, PMA, cytochalasin D, or latrunculin A was measured by immunofluorescence flow cytometry. A representative of three separate experiments is shown.