Figure 3.
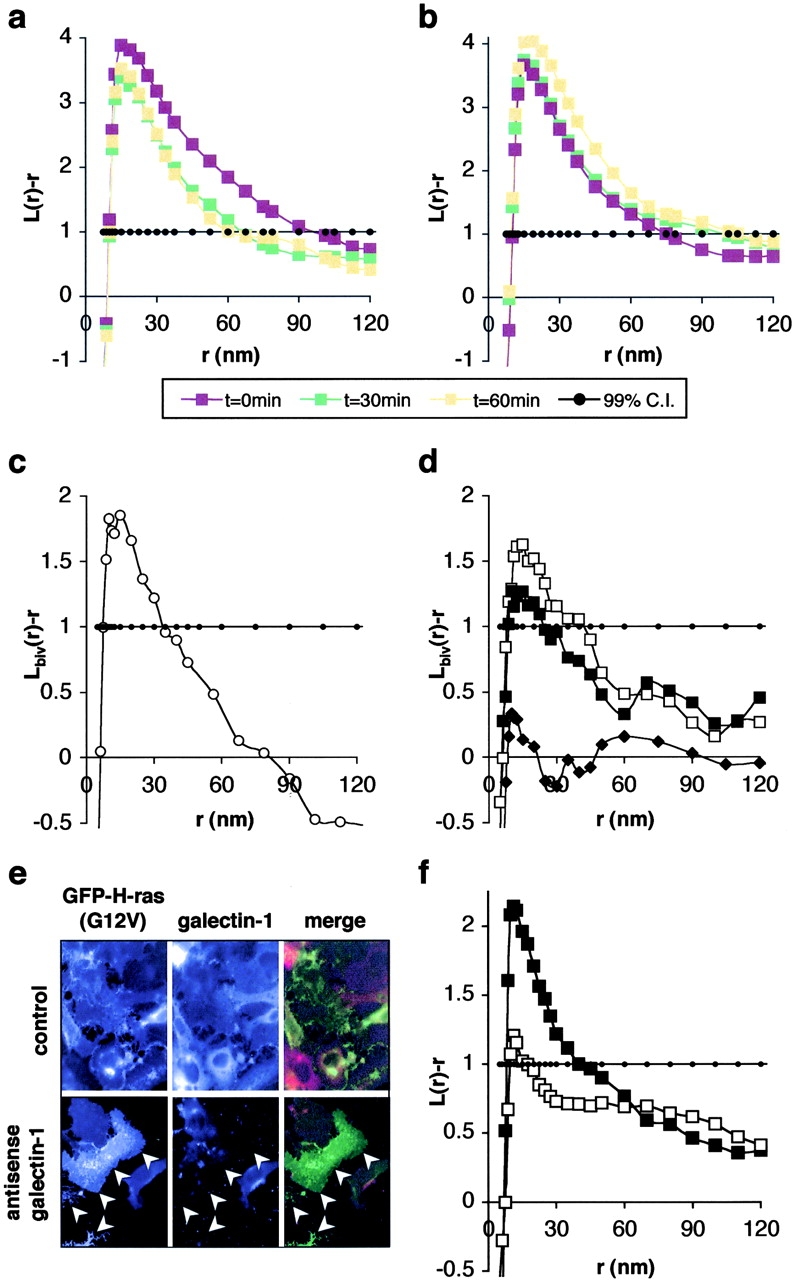
H-ras also occupies nonraft microdomains. Clustering of GDP-bound H-ras (a; GFP-HG12) and activated H-ras (b; GFP-HG12V) changes little with cyclodextrin treatment. (c) Plasma membrane sheets expressing GFP-H-ras were labeled with anti-GFP–2 nm and anti-Ras–4 nm gold to derive expected values for L biv(r) − r when there is complete colocalization of antigens under these assay conditions. Plasma membrane sheets from cells coexpressing GFP-tH and H-ras were then labeled with anti-GFP–2 nm and anti-Ras–4 nm gold. Bivariate analysis shows extensive colocalization of wild-type, GDP-bound H-ras with GFP-tH (d, open squares); serum stimulated GTP-loading of H-ras decreases coclustering (d, closed squares). Constitutively active H-rasG12V shows no colocalization with GFP-tH, i.e., L biv(r) − r trends around zero (closed diamonds). (e) Transfection with antisense galectin-1 DNA results in loss of endogenous galectin-1 expression. Note the loss of galectin-1 labeling in the transfected cells (arrowheads) compared with control. (f) Activated H-rasG12V clustering is significantly reduced in the absence of galectin-1 expression (open squares) compared with control (closed squares). K-functions are means (n ≥ 8 for each condition) standardized on the 99% CI for univariates and 95% CI for bivariates (closed circles in all panels).
