Figure 2.
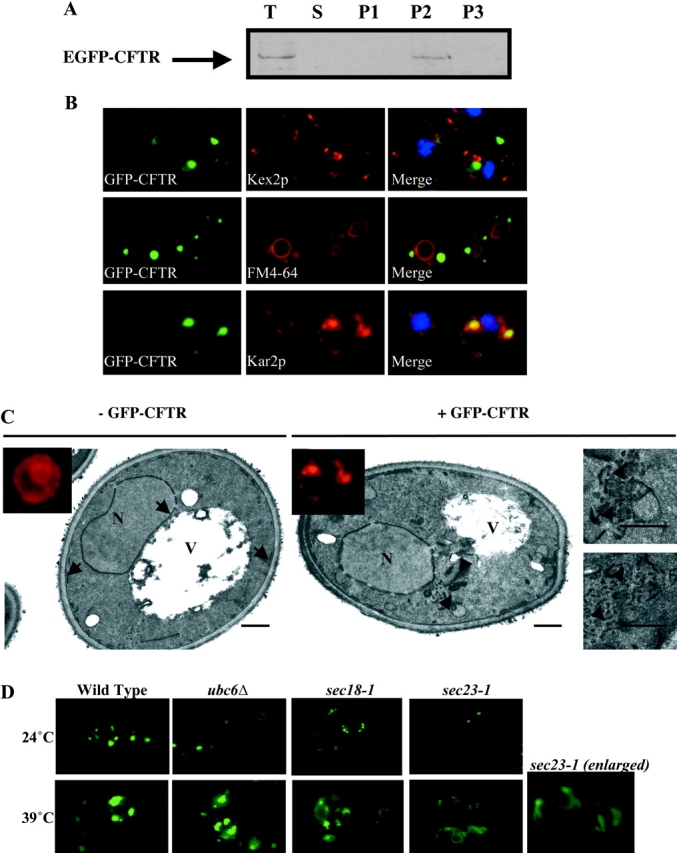
EGFP-CFTR localization depends on functional Sar1p/COPII machinery. (A) Yeast expressing EGFP-CFTR was subjected to membrane fractionation. A sample of each fraction was processed by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membrane, and immunoblotted with anti-CFTR antibody. T; total lysate. S; supernatant after high speed centrifugation. P1, P2, P3; pellets after low speed, medium speed, and high speed centrifugation, respectively. EGFP-CFTR is recovered exclusively in the membrane fraction. (B) Wild-type yeast expressing EGFP-CFTR was grown to log phase and processed for immunofluorescence using anti-Kar2p or anti-Kex2p antibodies, or was incubated with the fluorescent dye FM 4–64 for 45 min at 0°C, followed by 1 h at 24°C to stain the vacuole. EGFP-CFTR colocalizes only with the ER marker Kar2p. (C) Wild-type yeast transformed with pCU426CUP1 (− EGFP-CFTR) or with pCU426CUP1/EGFP-CFTR (+ EGFP-CFTR) was grown to log phase, induced, and processed for immunofluorescence with anti-Kar2p antibodies (insets) and for electron microscopy. Kar2p shows typical ER localization in − EGFP-CFTR cells, but distributes to punctate structures in + EGFP-CFTR cells. Cells without EGFP-CFTR contain normal ER (arrows), but cells expressing EGFP-CFTR show accumulation of membranous elements (arrowheads). Bar, 0.5 μm. (D) Wild-type, ubc6Δ, sec18–1 ts, and sec23–1 ts yeast transformed with pCU426CUP1/EGFP-CFTR was grown to log phase and induced at permissive (24°C) or restrictive (39°C) temperature. Live yeast were then imaged by fluorescence microscopy. EGFP-CFTR localizes to ER subdomains in wild-type, ubc6Δ, and sec18–1 ts yeast grown at permissive or restrictive temperatures. EGFP-CFTR localizes to ER subdomains in sec23–1 ts yeast grown at permissive temperature, but is diffusely distributed throughout the ER in sec23–1 ts yeast grown under restrictive temperature.
