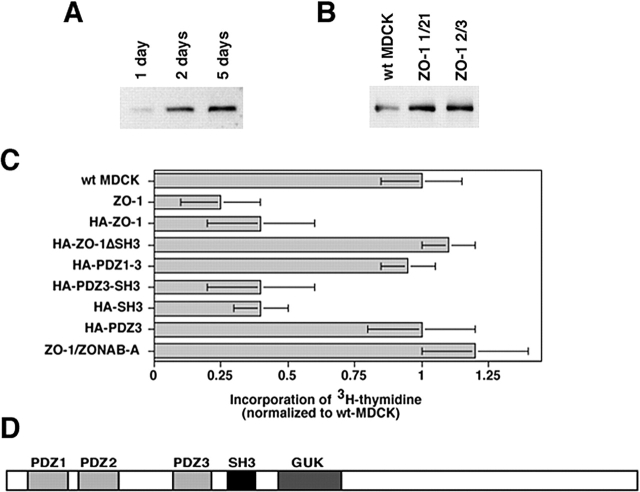
Figure 2.
Regulation of proliferation by ZO-1. (A and B) Expression of ZO-1 in wild-type and transfected MDCK cells. Wild-type MDCK cells (A) or wild-type (wt MDCK) and ZO-1–overexpressing (ZO-1 1/21 and ZO-1 2/3) cells (B) were grown for the indicated number of days as described in Fig. 1 A. Cells were then harvested, and equal amounts of protein were loaded on SDS-PAGE gels for analysis of ZO-1 expression by immunoblotting. Note that ZO-1 was overexpressed in transfected proliferating cells to a similar extent as it was up-regulated in mature monolayers. (C) Incorporation of [3H]thymidine by low density MDCK cells stably transfected with ZO-1 or HA-tagged ZO-1 with (HA-ZO-1) or without (HA-ZO-1ΔSH3) the SH3 domain, or constructs containing specified domains. ZO-1/ZONAB indicates data obtained from double transfected cells overexpressing both proteins. Data were normalized to wild-type cells (shown are means ± 1 SD of at least three independent clones per construct that were analyzed in three independent experiments with quadruplicate cultures). Note that all cell lines expressing constructs containing the SH3 domain of ZO-1 exhibited significantly reduced [3H]thymidine incorporation (t test; P < 0.05). (D) Domain structure of ZO-1. PDZ, PSD95-DlgA-ZO-1 homology domain; SH3, src homology domain 3; GUK, guanylate kinase homology domain.