Figure 8.
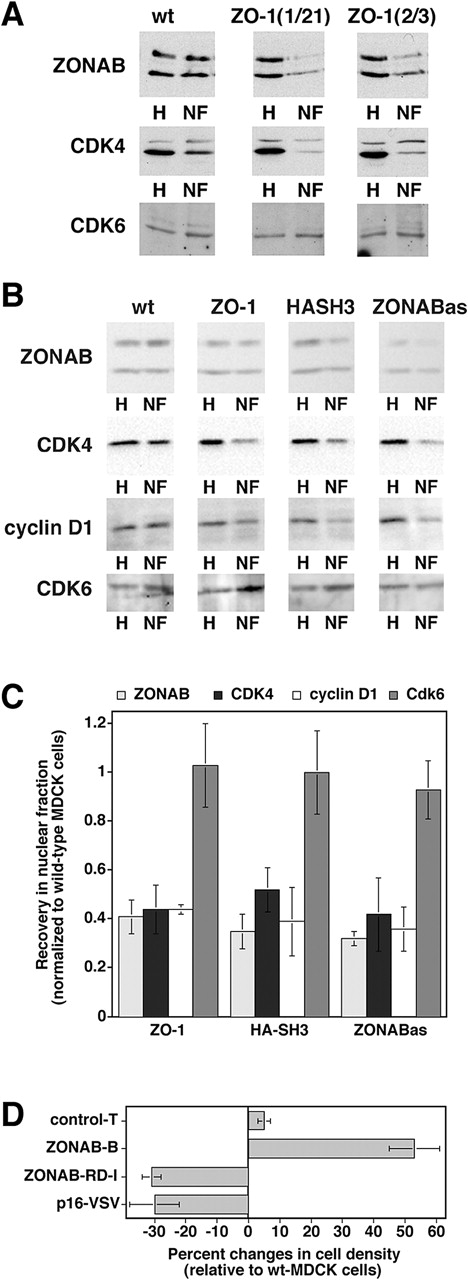
Regulation of CDK4 accumulation in the nucleus. (A) Nuclear fractions isolated from low density wild-type and ZO-1–overexpressing MDCK cells were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. Equal amounts of protein were loaded for all homogenates and for all nuclear fractions. The weak upper band in the CDK4 blot is a background band that was only detected by early batches of the commercial anti-CDK4 antibody, but not by later ones (see panel B for comparison). (B) Wild-type cells, clones transfected with cDNAs for either ZO-1 or the HA-tagged SH3 (HASH3), or cells expressing antisense ZONAB RNA (ZONABas) were grown, franctionated, and analyzed as in the experiment shown in A. To increase the sensitivity and accuracy of quantification, higher amounts of nuclear protein were loaded in B as compared with A to obtain bands with a similar intensity. (C) Quantification of nuclear accumulation. Immunoblots such as those shown in B were quantified by densitometric scanning, and the ratio of nuclear versus total signal was calculated. For each experiment, the ratio obtained from wild-type cells was set to 1 and the other cell lines were normalized to this value. Shown are averages ± 1 SD from at least three independent experiments. The values obtained for ZONAB, CDK4, and cyclin D1 in ZO-1, HA-SH3, and ZONABas cells were significantly different from those of wild-type cells with a confidence level of P < 0.02. (D) Reduced cell density in cells expressing a CDK4 inhibitor. Wild-type and transfected MDCK cells were grown as in Fig. 5 C, and were then harvested and counted. The cell number per cm2 of culture was calculated and expressed as percent changes relative to wild-type MDCK cells. Two independent clones expressing VSV-tagged p16-INK4a were analyzed in two independent experiments performed in triplicate. For comparison, the values of ZONAB-overexpressing or depleted clones from Fig. 5 are also shown. Note that expression of p16-INK4a significantly reduced the final cell density (t test; P < 0.05).
