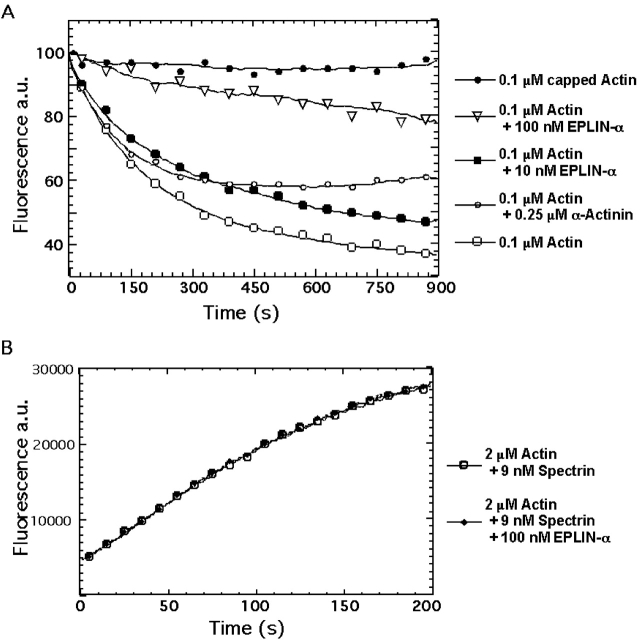
Figure 5.
Effect of EPLIN on actin filament depolymerization and barbed-end elongation. (A) Time course of the depolymerization of actin filaments in the presence of EPLIN, capping protein, and α-actinin. Actin was polymerized with capping protein, EPLIN, or α-actinin, and was then diluted 20-fold into polymerization buffer to initiate depolymerization. The final protein concentration in the samples were 0.1 μM actin, ± 0.15 μM capping protein, ± 10 or 100 nM GST-EPLIN-α, and ± 0.25 μM α-actinin. The actin polymer concentration was monitored over time using pyrene fluorescence. (B) Time course of actin filament elongation from barbed ends provided by spectrin-actin seeds. Samples in polymerization buffer contained 2 μM actin (5% pyrene labeled), 9 nM spectrin-actin seeds, and ± 100 nM EPLIN-α. In the presence of capping protein, actin polymerization was inhibited by <90% (not depicted).