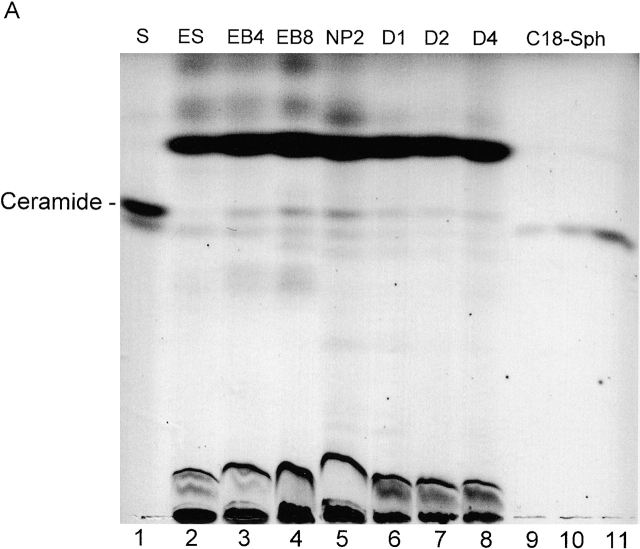
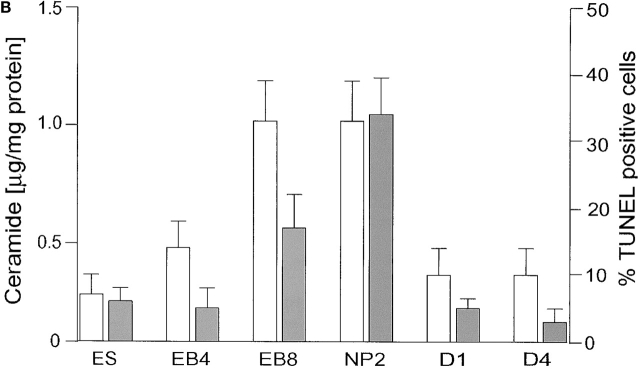
Figure 3.
Ceramide content and apoptosis during in vitro neuronal differentiation of ES cells. (A) Neutral lipids were purified from differentiating ES cells and a lipid amount corresponding to 750 μg of cellular protein/lane separated by HPTLC in the running solvent CH3Cl/HOAc (9:1, vol/vol). Lipids were stained with the cupric acetate reagent. Ceramide (open bars) was quantified by densitometric analysis and comparison with known amounts of standard lipid (N-oleoyl sphingosine). Lane 1, ceramide standard from bovine brain; lane 2, fibroblast-freed ES cells, after 4 d in culture; lane 3, EBs at the EB4 stage; lane 4, EBs at the EB8 stage; lane 5, NPs at the NP2 stage; lanes 6–8, three terminal differentiation stages, 24 (D1 stage), 48 (D2 stage), and 96 h (D4 stage) on cultivation of NP cells in serum-containing medium; lanes 9–11, N-oleoyl sphingosine, 250, 500, and 1,000 ng, respectively. (B) Lipids were extracted from differentiated ES cells and the amount of ceramide quantified using the DAG kinase assay. Apoptosis (solid bars) was determined by TUNEL staining. For HPTLC, DAG kinase, and TUNEL analyses, experiments were performed with five independent ES cultures. The bars show the standard mean and deviation of percentage of TUNEL-positive cells that were counted in five areas of 200 cells in each experiment.