Figure 4.
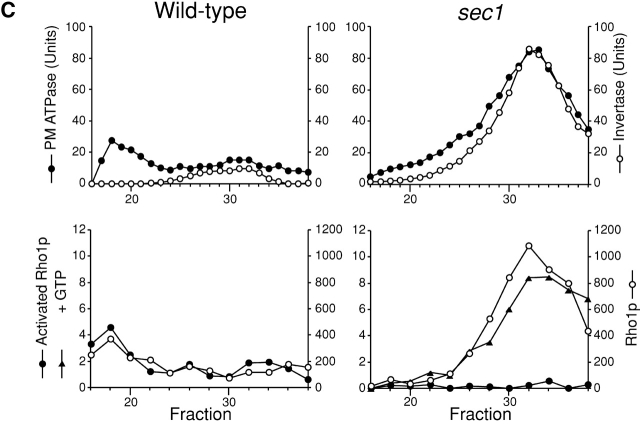
Localization of activated Rho1p detected with the purified anti-actRho1p antibody. (A) Affinity purification of the anti-actRho1p antibody. Antibody was raised against purified recombinant Rho1 (G19V) protein. Antiserum was loaded on an affinity column to which Rho1 (G19V) protein had been bound. The bound antibody was eluted, applied to another column charged with wild-type Rho1 protein, and the flow-through fractions were collected. (B) Immunoprecipitation of Rho1p with the anti-Rho1p (left), or the anti-actRho1p (right) antibody in the presence (+) or absence (−) of GDP and GTP-γS. Rho1p was detected by immunoblotting analysis with the guinea pig antiserum against Rho1p. (C) Immunoprecipitation of activated Rho1p. Wild-type (left) or sec1 mutant (right) cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The cells were lysed in the presence or absence of 4 μM GTP, and fractionated by differential centrifugations. The high-spin pellet was applied to a Sephacryl™ S-1000 column without GTP, and 3-ml fractions were collected. Top panels, distribution of plasma membrane ATPase (closed circles) and invertase (open circles). Bottom panels, the distributions of activated Rho1p (closed circles and triangles) and total Rho1p (open circles). Aliquots of each fraction were assayed by immunoprecipitation with the anti-actRho1p, and detected by immunoblotting analysis with the guinea pig antiserum against Rho1p. The relative amount was quantified with a cooled CCD camera (LAS-1000plus; Fuji Photo Film).