Figure 5.
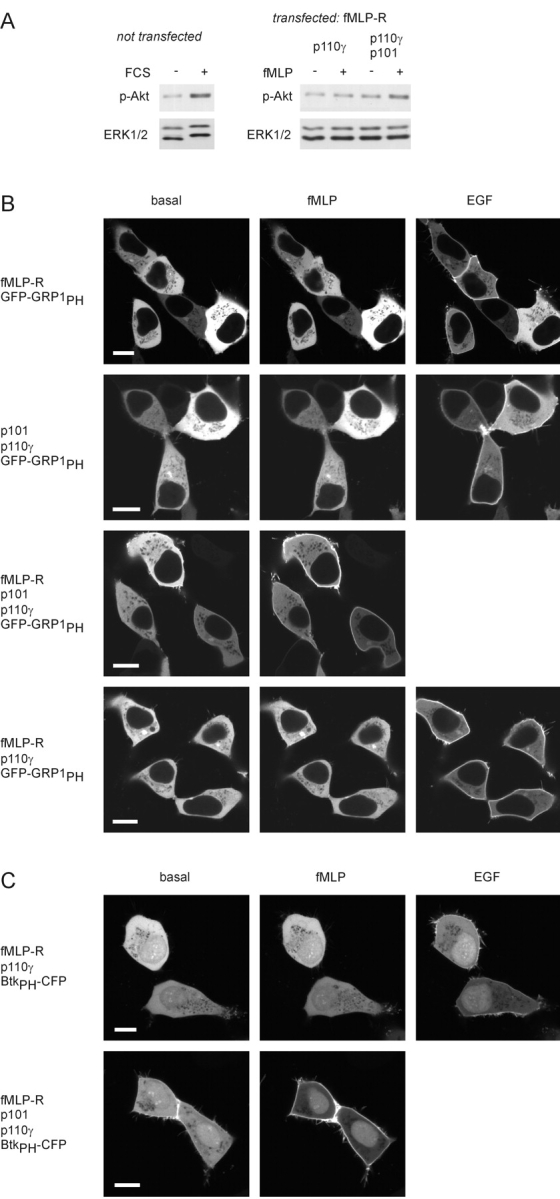
Activation of PI3Kγ by a G protein–coupled receptor. (A) Akt phosphorylation. Whole-cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody that specifically recognizes the phosphorylated form of Akt. Equal loading was shown by using an anti-ERK antibody. Left; FCS-induced Akt phosphorylation in untransfected HEK cells. Right; fMLP-induced Akt phosphorylation in cells expressing the fMLP receptor and only the catalytic (p110γ) or both PI3Kγ subunits. (B) Membrane recruitment of the PtdIns-3,4,5-P3–binding PH domain of GRP1. HEK 293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding the PH domain of GRP1 fused to GFP (GFP-GRP1PH), and the human fMLP receptor (fMLP-R), p110γ, and p101 in different combinations. The localization of the GFP-GRP1PH was monitored before and after the addition of 1 μM fMLP and 100 ng/ml EGF (added 8 min later) by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Pictures were taken 4 min after addition of either agonist. Images of typical experiments are shown (white bars, 10 μm). (C) Membrane recruitment of the PtdIns-3,4,5-P3–binding PH domain of Btk. Instead of GFP-GRP1PH, the PH domain of Btk fused to CFP (BtkPH-CFP) was used as a PtdIns-3,4,5-P3 sensor.
