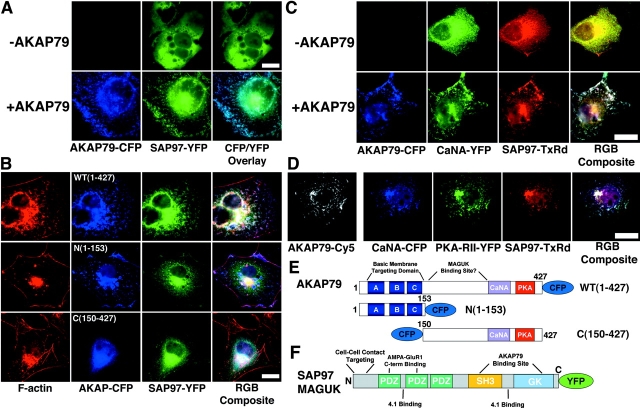
Figure 6.
Targeting of SAP97 to the CaN–AKAP79–PKA membrane cytoskeleton signaling complex. (A) AKAP79 regulates plasma membrane targeting of SAP97. SAP97–YFP (green) is primarily cytoplasmic when expressed alone (−AKAP79) but is targeted to the membrane ruffles in association with AKAP79–CFP (+AKAP79, blue) in live COS7 cells (CFP/YFP Overlay). (B) AKAP79 regulates targeting of SAP97 to the cortical membrane cytoskeleton through determinants that lie COOH terminal to the AKAP NH2-terminal targeting domain. SAP97–YFP (green) is targeted to the membrane ruffles enriched in F-actin (Texas red–phalloidin, red) in association with AKAP79–CFP (WT[1–427], top row, colocalization of SAP97, AKAP, and F-actin, seen as white in RGB composite panel). SAP97–YFP (green) is cytoplasmic when expressed with AKAP79(153)–CFP (blue) NH2-terminal domain, which targets to F-actin membrane ruffles (N[1–153], middle row, colocalization of (1–153) with F-actin, seen as pink in RGB composite panel) or an untargeted CFP–(150–427) AKAP79 fragment (C[150–427], bottom row). (C) AKAP79 regulates cortical colocalization of SAP97 with CaN in COS7 cells. CaNA–YFP (green) and myc–SAP97 (TxRd, red) are both cytoplasmic when expressed alone (−AKAP79) but are colocalized at the plasma membrane with each other and AKAP79–CFP (blue) in cells expressing all three proteins (+AKAP79), seen as white in the RGB composite. (D) AKAP79 coordinates targeting of CaN, PKA, and SAP97 to the same plasma membrane structures in COS7 cells. AKAP79 (anti-79, Cy5, monochrome) mediated membrane colocalization of CaNA–CFP (blue), PKA-RII–YFP (green), and myc–SAP97 (TxRd, red), seen as white in the RGB composite panel. Diagrams showing structures of the (E) AKAP79–CFP WT(1–427), N(1–153), and C(150–427) and (F) SAP97–YFP fusion proteins used above. Relevant cellular targeting, protein binding domains, and other structural motifs are indicated for both AKAP and SAP97 (see Results and Discussion for more details). Bars: (A and B) ∼15 μm; (C and D) ∼20 μm.