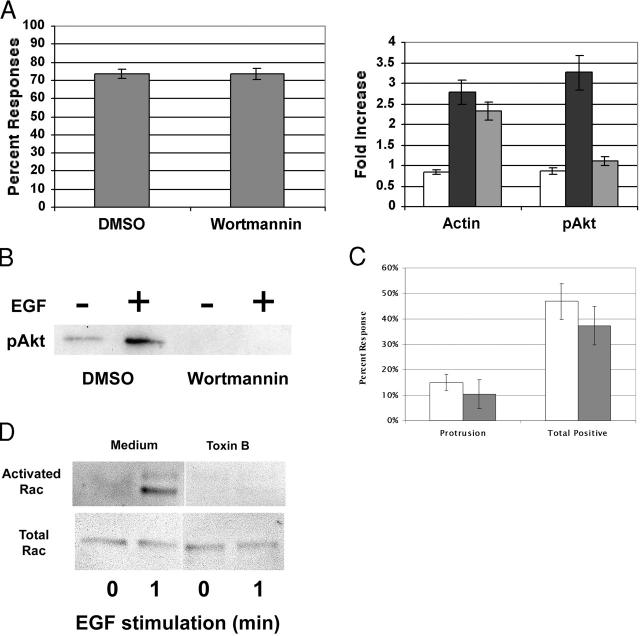
Figure 4.
The EGF bead response is PI3-kinase and rho family GTPase independent. (A) MTLn3:EGFR cells were starved for 1 h, and then treated with DMSO or 100 nM Wortmannin for 15 min. Cells recovered for 1 h, before being treated with either EGF beads for 5 min (A) or 10 nM soluble EGF (B) for 3 min. (A, left) The percentage of cells responding to beads treated with Wortmannin or DMSO. Data represent the mean ± SEM from >120 cells in three separate experiments. (A, right) Wortmannin effects on actin polymerization and phosphoAkt near beads. BSA beads (white), or EGF beads (black and gray), were given to cells that were pretreated with DMSO (white, black) or 100 nM Wortmannin (gray). The relative increase in staining for F-actin and pAkt near the beads compared with plasma membranes far from the beads was measured. Data represent the mean ± SEM from >60 cells in two or more separate experiments. (B) Cells untreated or treated with 10 nM soluble EGF and Wortmannin were lysed, and the whole cell lysates were probed for pAkt. (C) MTLn3:EGFR cells were starved for 1 h, and then treated with DMSO (white) or 50 ng/ml Toxin B (gray) for 1 h. The cells were then stimulated for 80 s, and the response was then analyzed. Data represent the mean ± SEM from >120 cells in four or more separate experiments. (D) Cells untreated or treated for 1 min with 5 nM soluble EGF and Toxin B were lysed and probed for activated rac by GST-CRIB pulldown (top) or total rac content (bottom) as described in Materials and methods.