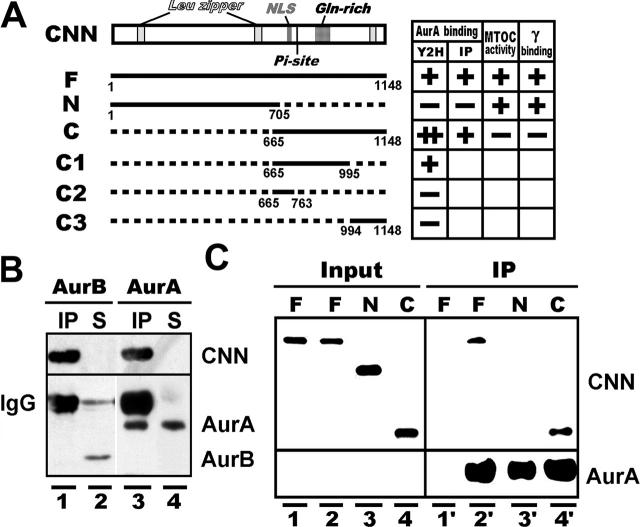
Figure 1.
Interaction of Aurora-A with CNN and γ-tubulin. (A) A map of CNN and its deletion constructs capable of association with Aurora-A assayed by yeast two-hybrid screening (Y2H) and immunoprecipitation (IP). Microtubule-nucleating activity (MTOC activity) and γ-tubulin interaction (γ binding) are also summarized on the right. CNN contains characteristic regions, including leucine zipper motifs (Leu zipper), a potential nuclear localization signal (NLS), a putative Aurora-A phosphorylation site (Pi-site), and a glutamine-enriched region (Gln-rich). Numbers indicate the positions of amino acids. (B) HA-tagged CNN binds to Aurora-A (lanes 3 and 4), but not Aurora-B (lanes 1 and 2), in S2 cells. Proteins in immunoprecipitated (IP) and nonprecipitated supernatant (S) fractions, prepared from HA-CNN–expressing (lanes 1 and 3) and –nonexpresssing (lanes 2 and 4) cells, were identified by blotting with HA, Aurora-A, and Aurora-B antibodies. (C) Aurora-A binds to the COOH-terminal domain of CNN. In vitro synthesized full (F), NH2-terminal (N), and COOH-terminal (C) domains of CNN (Input, lanes 1 to 4) were mixed with (IP, lanes 2′ to 4′) and without (IP, lane 1′) His-tagged Aurora-A purified from bacteria.