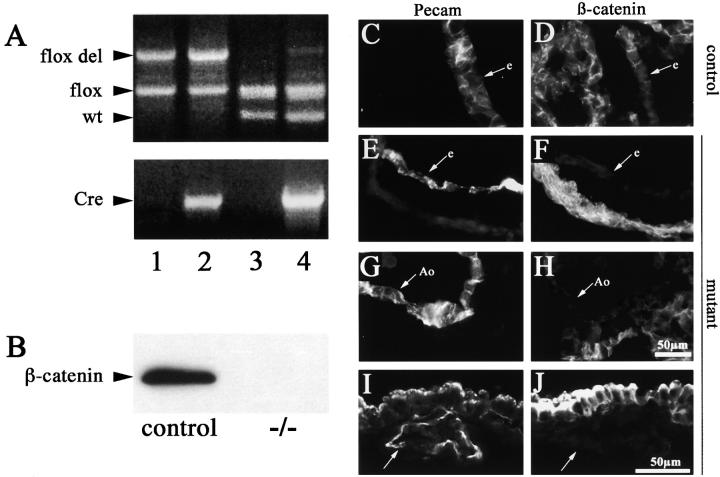
Figure 1.
Cre recombinase efficiently recombines the β -catenin flox allele in vivo. (A) Genomic PCR on E10.5 embryos from Tie2-Cre x β-catenin flox/flox crossings for the β-catenin gene and for Tie2-Cre gene. The four lanes represent the four different genotypes obtained: β-catenin flox del/flox, Cre − (+/−, lane 1), β-catenin flox del/flox, Cre + (−/−, lane 2), β-catenin flox/wt, Cre − (+/+, lane 3), and β-catenin flox/wt, Cre + (+/−, lane 4). In this last lane, note the presence of the recombined β-catenin flox del band when the flox allele is in the presence of Tie2-Cre recombinase. (B) Western blot of β-catenin protein in endothelial cell lines established from wt (control) and β-catenin flox/flox del, Tie2-Cre + embryos (−/−). (C-J) Immunofluorescence for anti-PECAM and anti-β-catenin antibodies on serial cryosections from wild-type (+/+, control) and β-catenin flox/flox del, Tie2-Cre + (−/−, mutant) E10.5 embryos. Heart sections show positive staining of the endocardium (e) with PECAM antibodies in both control (C) and β-catenin −/− (E) animals. β-Catenin staining is undetectable in mutant embryos (F). β-Catenin is also absent in the dorsal aorta (G and H, Ao) and in the yolk sac vessels (I and J, arrow) of the mutant embryos. Bar in H refers to C–H, and bar in J refers to I and J.