Figure 2.
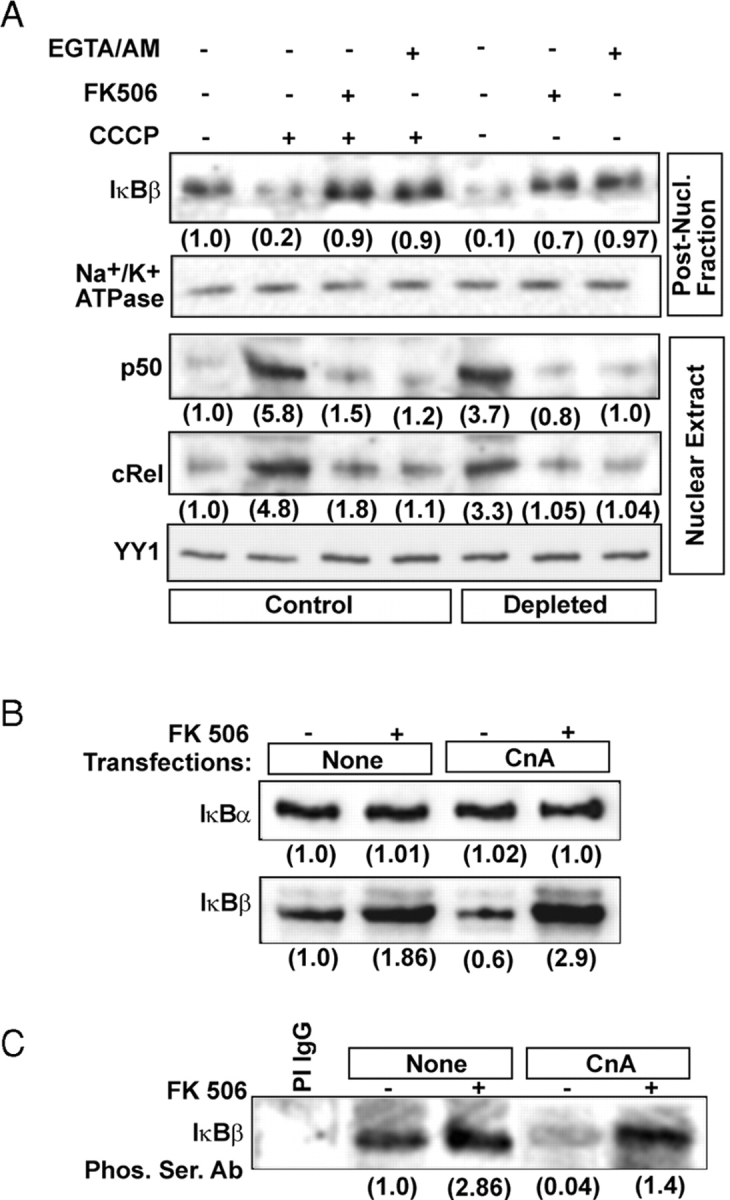
Role of Ca2 + and Cn on dephosphorylation of IκBβ and steady-state levels of NFκB/Rel proteins. (A) Control and CCCP-treated (25 μM for 2 h) C2C12 cells were incubated with or without added FK506 (10 nM) or EGTA/AM (30 μM). Alongside mtDNA-depleted C2C12 cells were also incubated for 2 h with or without inhibitors. Nuclear and postnuclear protein fractions (30 μg each) were subjected to immunoblot analysis using indicated antibodies. (B) Postnuclear fractions (30 μg each) of C2C12 cells transfected with CnA cDNA and treated with FK506 as in A were analyzed by immunoblot analysis using antibodies against IκBα or IκBβ. (C) Postnuclear fractions (0.5 mg protein) from control and transfected cells were immunoprecipitated with IκBβ antibody as described in Materials and methods. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using Ser-phosphate antibody. (D) The in vivo effects of CnA on IκBβ phosphorylation. C2C12 cells transfected with WT and ΔPEST domain mutant IκBβ or CnA cDNAs were labeled with 32P-orthophosphate and treated with or without FK506 (10 nM) as described in Materials and methods. The top panel shows the extent of 32P labeling of IκBβ detected by autoradiography, and the middle and bottom panels show the immunoblot analyses for the levels of IκBβ and CnA, respectively. The numbers in parentheses in A–D underneath the gel bands show relative band intensities determined by imaging through Bio-Rad Laboratories Fluor-S Imager.

