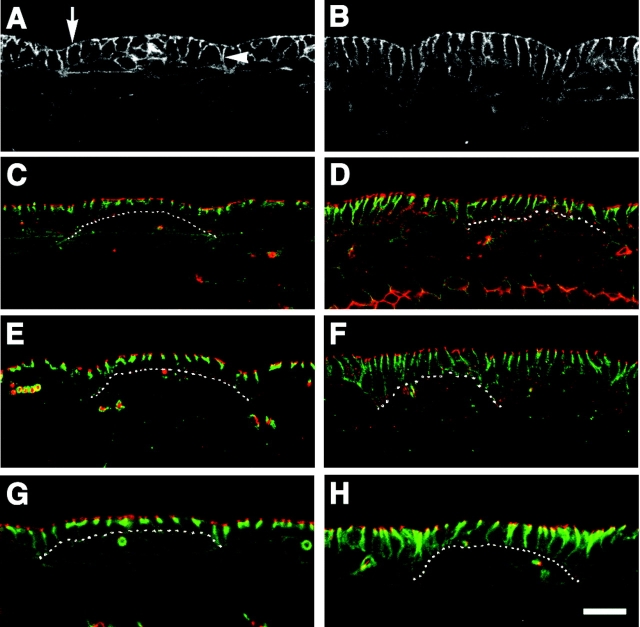
Figure 2.
SJ markers are mislocalized in Gli mutants. All images are of stage 15 embryos and the epidermis is viewed in cross section. (A, C, E, and G) Wild-type embryos. (B, D, F, and H) Homozygous Gli AE2Δ 45 mutants. (A and B) α-Spectrin staining reveals general epithelial morphology. Wild-type epithelial cells have columnar morphology, and α-spectrin labels both the (A, arrow) apical and (B, arrowhead) lateral membrane domains. In Gli mutants, epithelial cells are slightly taller and have a more uniform columnar shape, whereas the localization pattern of α-spectrin is (B) wild type. (C and D) Embryo stained for the SJ marker, Dlg (green) and the AJ marker; arm (red). The dotted line marks the basal surface of epithelial cells in a single abdominal segment. The stereotypic organization of AJs positioned apical to pSJs can be observed in (C) wild-type embryos. In Gli mutants, Dlg localization is disrupted and has diffused basally, whereas arm localization is (D) normal. (E and F) Embryos doubled stained for the pSJ marker Nrx (green) and arm (red). Nrx is also mislocalized in (F) Gli mutants. (G and H) Embryos stained for the pSJ marker Cora (green) and the AJ marker DE-cad (red). Just like Dlg and Nrx, the pSJ marker Cora is mislocalized in Gli mutants; however, the localization of DE-cad is (H) unaffected. Bar, 10 μm.