Figure 5.
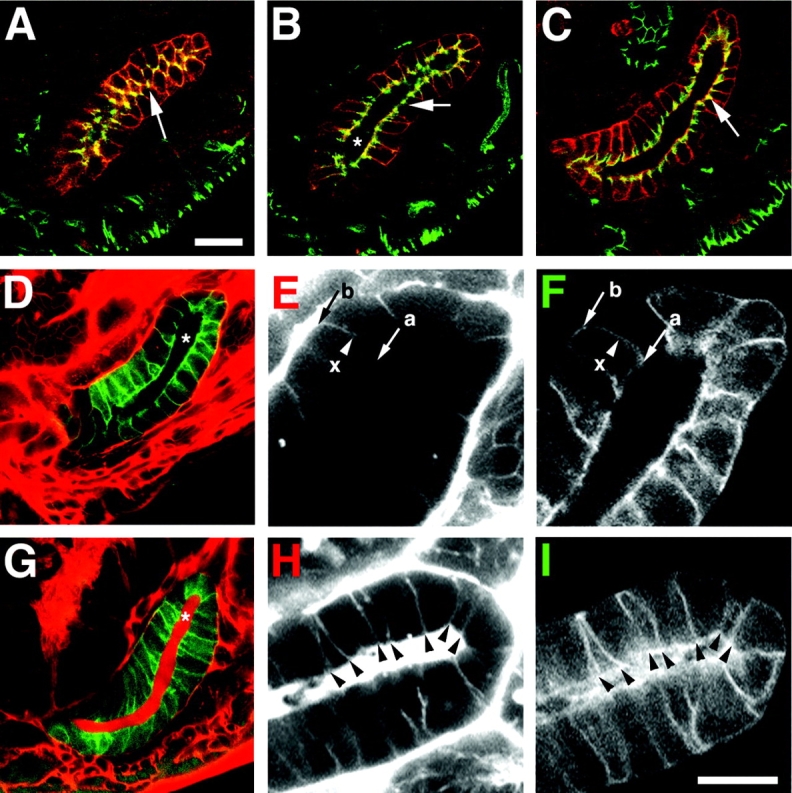
The integrity of the salivary gland transepithelial barrier is disrupted in Gli mutants. (A–C) Fixed, wild-type, stage 17, da.G32:UASgapGFP embryos, stained for gapGFP (red), which marks salivary gland epithelial membranes, and (A and B, green) Gli or (C, green) Cora. Colocalization of gapGFP with Gli or Cora is yellow. (A) Gli is localized to the tricellular corners of salivary gland epithelial cells (en face view) as in the epidermis (arrow). (B) Longitudinal section of the salivary gland shown in A reveals the gland lumen (asterisk) and localization of Gli to the pSJ domain (arrow). (C) Cora labels the apical portion of the lateral membrane similar to Gli (compare arrows in B and C). (D–I) Live, wild-type da.G32:UASgapGFP (D–F) and Gli AE2Δ 45: da.G32:UASgapGFP homozygous mutant (G–I) embryos whose hemocoels have been injected with 10-kD rhodamine–dextran conjugate to evaluate the integrity of the salivary gland transepithelial barrier. Embryos were imaged within 10 min of injection. (D) In wild type, the tracer (red) is excluded from the lumen (asterisk) of the salivary gland, which expresses gapGFP (green). (E) High magnification of the salivary gland (red channel) reveals the tracer, which penetrates between epithelial cells in a basal (b) to apical (a) direction, but only as far as the presumptive pSJ domain (x). Compare position of pSJ domain in C (arrow) with the dye block site (x) in E. (F) Green channel, the dye block site (x) is superimposed on the salivary gland epithelial cell profiles. (G) In homozygous Gli mutant embryos, the transepithelial barrier function of the salivary gland (green) is impaired and the tracer (red) fills the gland lumen (asterisk). (H and I) In high magnification views of the salivary gland, the tracer (G, red channel) is observed to penetrate between cell–cell contacts of multiple consecutive (arrowheads) epithelial cells. Compare arrowheads in H with those in I (green channel). Bars: (A–D and G) 20 μm; (E, F, H, and I) 10 μm.
