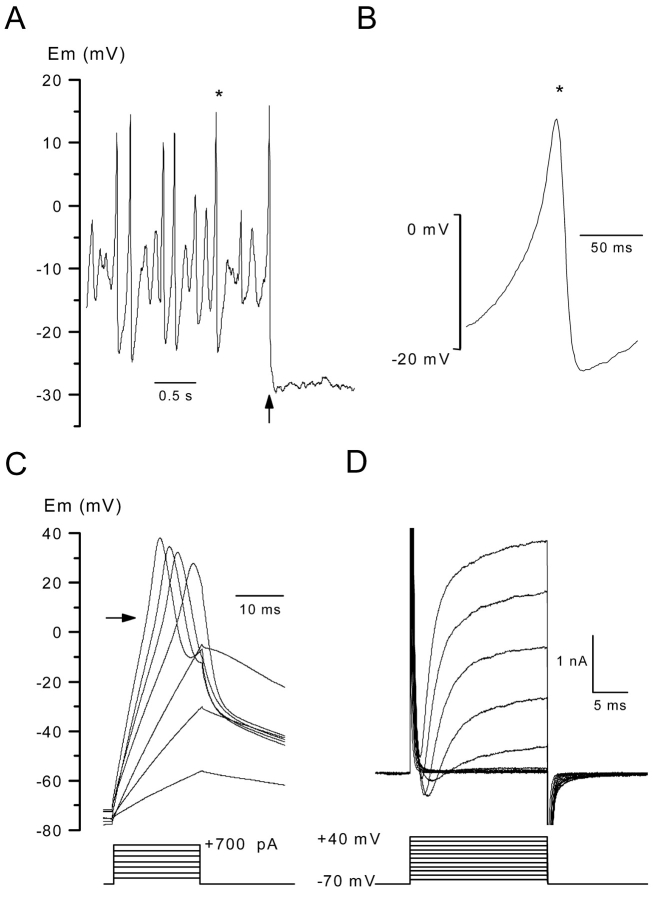
Figure 1.
Voltage responses and ionic currents in body wall muscle cells in the presence of standard saline. (A, left) Membrane potential was recorded in a muscle cell in the current clamp mode without current injection. The arrow indicates the time at which a negative hyperpolarizing current was injected. (B) A spontaneous spike indicated by a star in the left panel is shown on an expanded scale. (C) The internal potential was held at –70 mV by passing a constant negative current, and voltage responses were obtained in response to current injection of 20 ms duration in 100 pA increments. The arrow indicates an inflection point during the depolarizing phase. (D) Membrane currents were elicited on the same cell as in C under voltage clamp conditions by applying voltage pulses of 20 ms duration in 10-mV increments from a holding potential of –70 mV.