Figure 1.
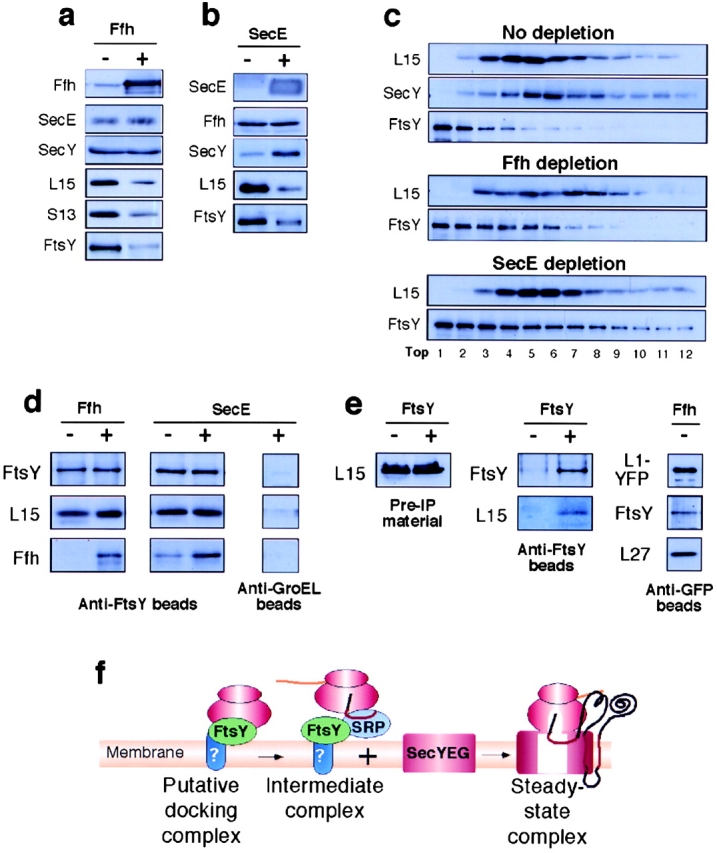
Accumulation of membrane-bound FtsY–ribosome complexes. Accumulation as analyzed by Western blotting (a, b, and c) and immunoprecipitation (d and e). (a and b) Accumulation of membrane-bound ribosomal proteins and FtsY in cells depleted of Ffh or SecE, respectively. (c) Sucrose density gradients of digitonin-solubilized membranes. (d) Coimmunoprecipitation of ribosomal proteins and Ffh with anti-FtsY antibodies. Purified membranes were solubilized by digitonin and the soluble material was incubated with anti-FtsY beads or anti-groEL beads as control. Immunoprecipitates were calibrated for equal amounts of FtsY by a separate semiquantitative Western blotting (not depicted) and then analyzed by Western blotting. (e) Control coimmunoprecipitation studies: total ribosomal fractions (left, membrane and cytosolic ribosomes, indicated as Pre-IP materials) from FtsY-depleted and nondepleted cells were coimmunoprecipitated with anti-FtsY beads and tested by Western blotting with anti-FtsY and anti-L15 antibodies (e, middle). (e, right) solubilized membranes from Ffh-depleted cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-YFP beads and the precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-GFP, anti-FtsY and anti-L27 antibodies. (f) Schematic representation of putative membrane-bound ribosomal complexes that form during and at the end of the ribosome targeting pathway.
