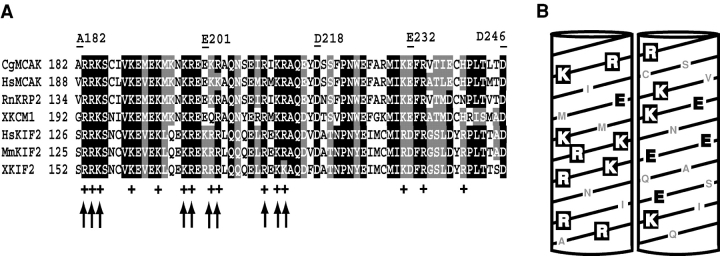
Figure 1.
The structural analysis of the MCAK neck. (A) Sequence alignment of the neck domain of seven Kin I kinesins: CgMCAK, C. griseus (residues A182-D246; GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. U11790); HsMCAK, Homo sapiens (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. U63743); RnKRP2, Rattus norvegicus (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. U44979); XKCM1, Xenopus laevis (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. U36485); HsKIF2, Homo sapiens (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. CAA69621); MmKIF2, Mus musculus (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. D12644); XKIF2, X. laevis (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. U36486). Identical residues are shaded in black, similar ones are shaded in gray. The 64-amino acid neck domain sequences are 50% identical and 75% similar. The + symbols indicate highly conserved positively charged amino acids in the neck domain. The arrows show residues that were substituted for alanine. The borders of deletions in the neck domain are indicated by flanking residue numbers above the neck alignment. (B) Two sides of a helical diagram of a highly charged hydrophilic helix (residues R183–Q215) found in the CgMCAK neck. Positively charged amino acids are white, negatively charged residues are black, and the other residues are gray.