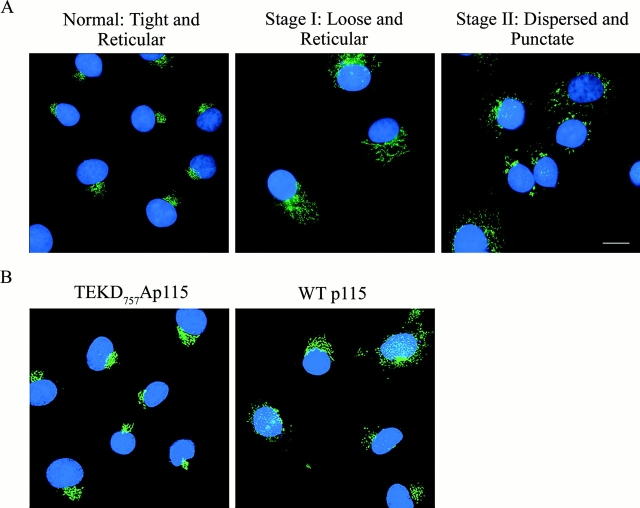
Figure 4.
Classification of Golgi morphology during apoptosis. (A) Untreated COS7 cells (left) were fixed and stained with a monoclonal antibody against GM130 (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33238 (blue). Note the tight perinuclear Golgi staining of untreated cells. After etoposide treatment for 24 h, two populations of cells were distinguished. In one population (middle), the Golgi apparatus is at an early stage of fragmentation where staining is loose, but still reticular and perinuclear. In the second population, the Golgi apparatus is completely dispersed and the resulting membrane fragments stain as punctate structures (right). (B) COS7 cells transfected with either wild-type p115 or the p115 TEKD757Ala mutant were treated with etoposide for 24 h. Cells were then stained and processed as above. Expression of the p115 TEKD757Ala mutant delayed both stages of Golgi fragmentation compared with control cells expressing wild-type p115. Bar, 10 μm.