Figure 1.
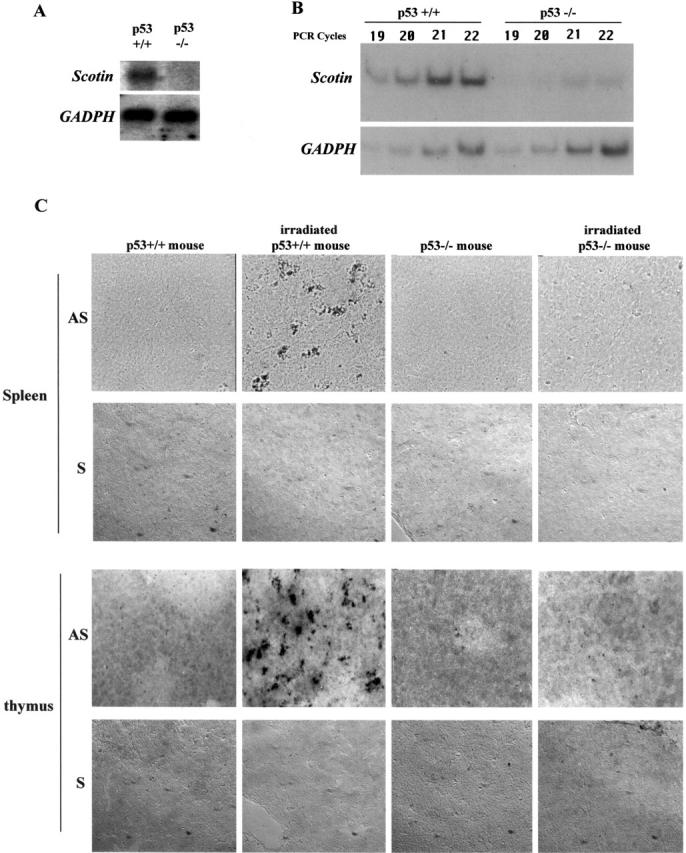
Scotin mRNA is induced after γ-irradiation in the spleen and thymus of normal mouse but not in p53 −/− mouse. p53 nullizygote (−/−) mice as well as wt (p53+/+) litter mates were exposed to 5 Gy γ-irradiation. Total RNA was extracted 3 h later from the spleen of each mouse. (A) Northern blot. 10 μg of total RNA was analyzed by hybridization with a mouse Scotin probe. After autoradiography, the blot was stripped and rehybridized with rat GAPDH probe. (B) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR. 0.5 μg of total RNA was analyzed by RT-PCR by incorporating [33P]dATP and using Scotin- or GAPDH-specific primers as described in Materials and methods. PCR reactions were stopped after different cycles to assess the linear amplification. PCR products were electrophoresed on 8% polyacrylamide gel before autoradiography. (C) In situ hybridization. Two p53+/+ male mice and two p53−/− male mice were exposed to 5Gy of whole body γ-irradiation. Spleen and thymus were removed 3 h after irradiation. Sections were incubated with a digoxigenin-labeled antisense (AS) Scotin RNA probe or with a digoxigenin-labeled sense (S) Scotin RNA probe. Sections were incubated with antidigoxigenin antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase. Scotin mRNA was then visualized by the addition of a precipitating substrate (NBT/BCIP).
