Figure 4.
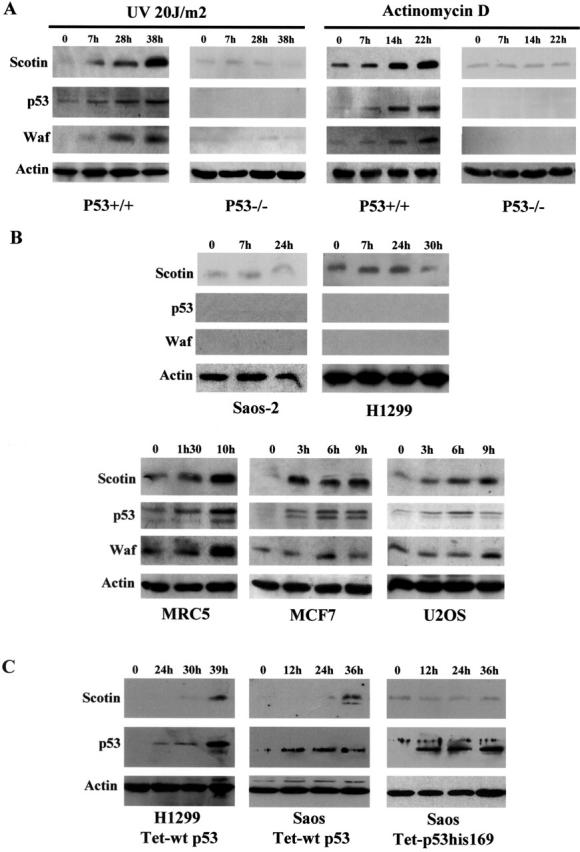
Scotin protein expression is induced in a p53-dependent manner. (A) Primary MEF expressing wtp53 induce Scotin after UV irradiation or Actinomycin D treatment. MEF (passage 2) from p53−/− and p53+/+ littermate mice were exposed to UV-C light (20 J/m2) or Actinomycin D (60 ng/ml), a potent p53 activator. Proteins were extracted at the indicated time after treatment and analyzed by Western blot. (B) Primary human fibroblasts and human tumor cell lines expressing functional p53 induce Scotin in response to Actinomycin D. The primary human fibroblast MRC5, the tumor cell lines (MCF7 and U2OS) expressing functional p53, and the tumor cell lines devoid of p53 expression (Saos-2 and H1299) were treated with 60 ng/ml of Actinomycin D. Proteins were extracted at the indicated time and analyzed by Western blot. (C) p53 expression is sufficient to induce human Scotin expression. Proteins were extracted at the indicated time after tetracycline induction from tetracycline-inducible p53 H1299 cells or Saos-2 cell lines described in Materials and methods. Membranes were probed in succession using anti-Scotin pAb, anti-p53 pAb, and anti-Waf mAb, as described in Materials and methods. To control loading and transfer efficiency, membranes were incubated with antiactin mAb.
