Figure 3.
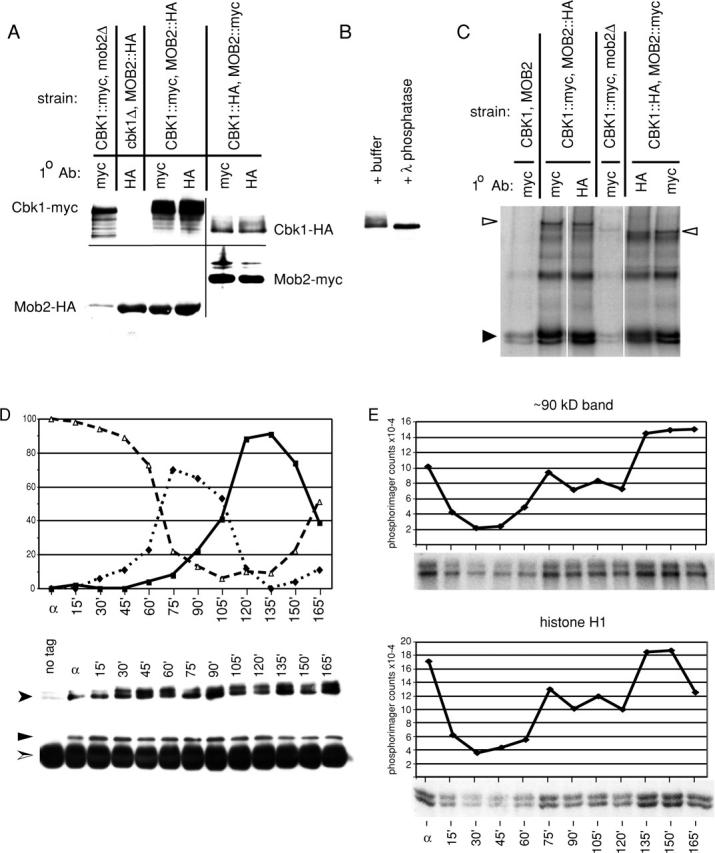
Mob2p physically associates with Cbk1p and is required for Cbk1p kinase activity and hyperphosphorylation. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of Mob2p and Cbk1p (FLY954 and FLY960), immunoprecipitation of Mob2p from cbk1Δ cells (FLY1005), and immunoprecipitation of Cbk1p from mob2Δ cells (FLY906). The faint HA signal in lane 1 is due to spill over from the neighboring lane. (B) Treatment of immunoprecipitated Cbk1p-HA with λ phosphatase, with λ phosphatase reaction buffer treatment as negative control. (C) Kinase activity present in immunoprecipitates of epitope-tagged Mob2p and Cbk1p. These kinase reactions were performed using the immunoprecipitates characterized by immunoblot shown in A. (D and E) Cells expressing Cbk1p-HA and Mob2-myc (FLY954) were synchronized in G1 (as described in Materials and methods). Anti-HA immunoprecipitations were conducted on extracts of these cells after normalization of protein concentrations. (D, top) Budding morphology at arrest (α) and after release from block. Percentages of unbudded cells are indicated by ▵, small budded cells by ♦, and large budded cells by ▪. (D, bottom) Anti-HA and corresponding anti-myc immunoblots of immunoprecipitated protein. Cbk1p-HA, shown by anti-HA immunoblot, is indicated by a filled arrowhead. Mob2-myc, shown by anti-myc immunoblot, is indicated by ▴. Immunoglobulin heavy chain is indicated by a split arrowhead. (E) Kinase activity present in immunoprecipitated Cbk1p-HA. The top two panels show phosphorylation of a ∼90-kD band, likely Cbk1p autophosphorylation, and the bottom panels show phosphorylation of histone H1. These kinase reactions were performed using the immunoprecipitates characterized by immunoblot (D).
