Figure 2.
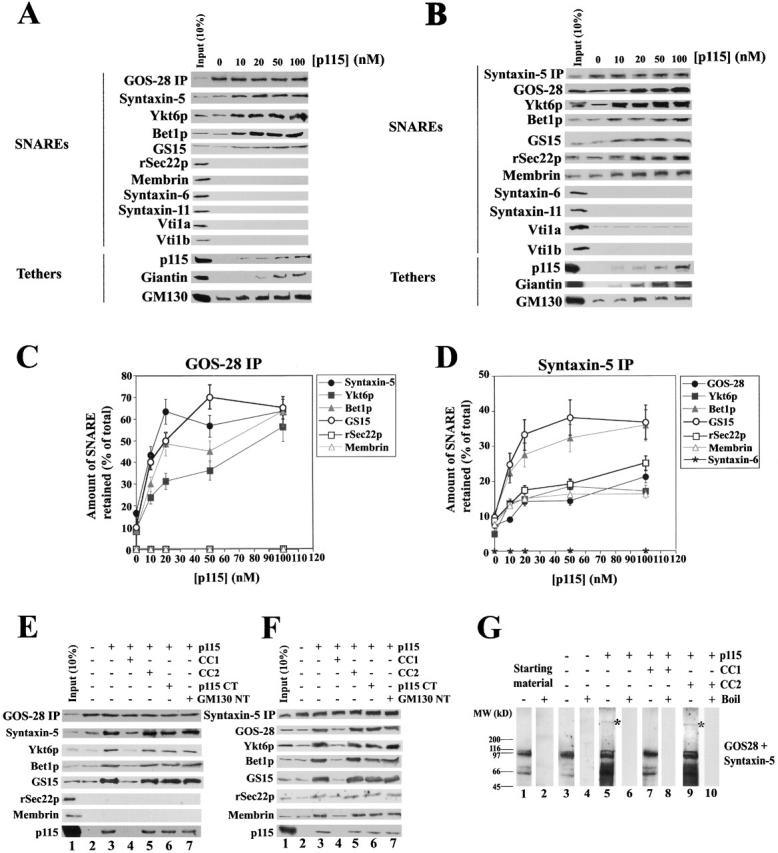
p115 stimulates specific SNARE complex formation in Golgi extracts. (A and B) Salt-washed RLGs that had been treated with NSF to disassemble cis-SNARE complexes were solubilized in Triton X-100 buffer and incubated with increasing concentrations of p115 (0–100 nM). GOS-28 (A) or syntaxin-5 (B) was immunoprecipitated, and the extent of coprecipitation of other Golgi SNAREs and tethers was determined by immunoblot. For the p115 immunoblot, the input (10%) lane reflects 10% of the maximum p115 concentration added (100 nM). (C and D) Quantitation of GOS-28 (C) and syntaxin-5 (D) immunoprecipitations. Amount of coprecipitated SNARE retained (% of total) as determined by densitometric scanning is plotted versus p115 (nM). Values represent means ± SEM (n = 3). (E and F) Golgi detergent extract (as in A) was incubated on ice with or without 100 nM p115 plus either buffer, 10 μM CC1 or CC2, 20 μM p115 CT (p115 COOH-terminal 75 aa), or GM130 NT (GM130 NH2-terminal 73 aa). GOS-28 (E) or syntaxin-5 (F) was immunoprecipitated, and the extent of coprecipitation of other Golgi SNAREs and p115 was determined by immunoblot. For the p115 immunoblot, the input (10%) lane reflects 10% of the maximum p115 concentration added (100 nM). (G) Salt-washed NSF-treated RLGs were incubated for 30 min at 37°C with or without 100 nM p115 plus or minus 10 μM CC1 or CC2. Reactions were stopped with SDS-PAGE sample buffer, incubated for 7 min at 25 or 95°C, and processed for immunoblot. Blots were probed with a mixture of anti–GOS-28 and anti–syntaxin-5 antibodies. Asterisk denotes a p115-induced high molecular weight species.
