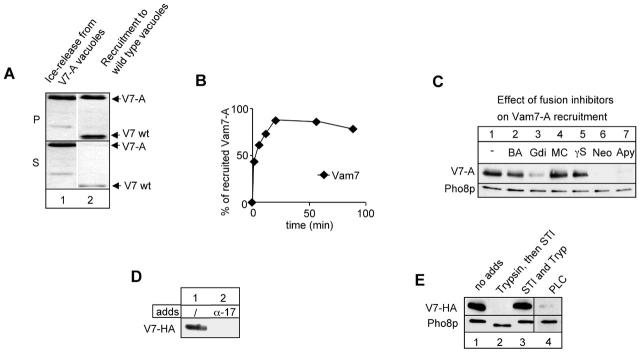
Figure 3.
Recruitment of soluble Vam7p to vacuoles. (A) Wild-type vacuoles (BJ3505) and Vam7-A vacuoles were incubated in the presence of ATP for 30 min on ice. Vacuoles were reisolated (20,000 g, 5 min, 4°C), and wild-type vacuoles were resuspended in supernatant removed from Vam7-A vacuoles and incubated for 60 min at 26°C. Then the reaction was centrifuged as before and analyzed for Vam7p in pellet (P) and supernatant (S). The second band in lane 1 is a degradation product of Vam7-A. (B) Time course of recruitment. Recruitment of Vam7-A to wild-type vacuoles was done as in A but for different time points. Immunoblots showing Vam7-A were quantified by densitometry and plotted. The total amount of Vam7p in the supernatant was set to 100%. (C) Gdi1p, ATP depletion by apyrase, and neomycin block Vam7p rebinding. Wild-type and Vam7-A vacuoles were preincubated as in A. The indicated inhibitors were added to the recruitment reaction at the following concentrations: BA, 2 mM BAPTA; Gdi, 300 μg/ml Gdi1p; MC, 10 μM microcystin LR; γS, 3 mM Mg-GTPγS; Neo, 500 μM neomycin; and Apy, 20 U/ml apyrase. The pellet was analyzed as before. (D) Priming is essential to create a Vam7 binding site. Wild-type vacuoles were primed on ice for 30 min in the absence or presence of antibodies to Sec17p (200 μg/ml), then reisolated and incubated with Vam7-HA containing supernatant generated in a parallel incubation, and processed as in the legend to Fig. 1 C. Immunoblots were decorated with antibodies to Pho8p to show equal amount of vacuole membranes in each lane. (E) Lipid and protein requirements for Vam7p recruitment. Acceptor vacuoles (12 μg) were primed on ice and resuspended in PS buffer with 150 mM KCl. Trypsin (Try; 10 μg/ml) was added either alone or in the presence of soybean trypsin inhibitor (STI; 100 μg/ml) and incubated with vacuoles for 30 min on ice. STI was then added to stop the digestion. One aliquot was incubated with 2.5 U/ml of the phosphoinositide-specific PLC (Sigma-Aldrich) to remove inositol head groups. Vacuoles were reisolated and used as acceptor membranes as before. Immunoblots were decorated with anti-Pho8p to show equal loading. Note that trypsin digestion caused a truncation of the cytoplasmic tail of Pho8p.