Figure 2.
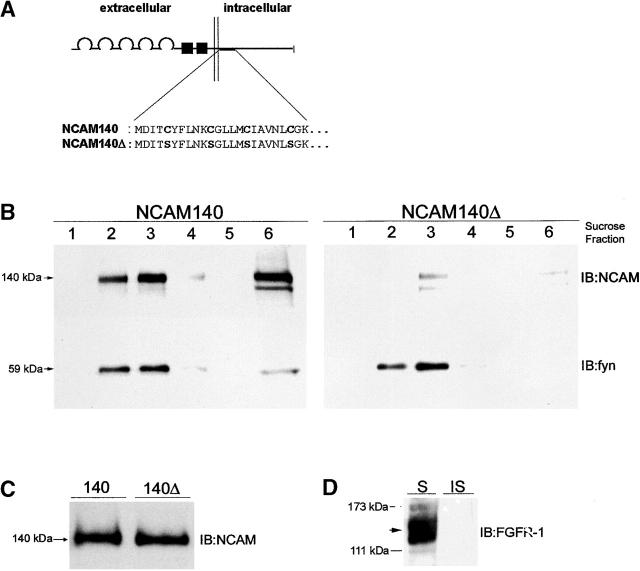
Mutation of NCAM140 palmitoylation sites abolishes NCAM140 raft association. (A) Schematic diagram of the structure of NCAM140 and NCAM140Δ. The plasma membrane is indicated by the pair of vertical lines. The semicircles represent the five Ig-like domains. The two fibronectin type III–like domains are shown as black boxes. The expanded segment shows the NH2-terminal sequence of the cytoplasmic domain and the four cysteines that were mutated to serines in the NCAM140Δ construct to remove all sites for palmitoylation. (B) Immunoblot analysis of sucrose gradient fractions of NCAM140- (left) and NCAM140Δ- (right) transfected CHO cells. NCAM140 is present both in the Triton X-100–insoluble low density raft fractions (lanes 2 and 3) and high density fraction (lane 6). To estimate the percentage of raft-associated NCAM140 versus total NCAM140, we normalized the densitometrically determined immunoblot intensity of the NCAM140 bands in the total cell lysate (C) and in the raft fractions (B, left, lanes 2 and 3) to the total protein subjected to SDS-PAGE. Relating the amount of NCAM140 present in lipid rafts to the total amount of NCAM140 revealed that ∼2% of the total NCAM140 protein is present in the lipid raft fractions. Analysis of the sucrose gradient fractions of NCAM140Δ-transfected cells shows a drastically reduced amount of NCAM in the low density fractions (lanes 2 and 3) and the high density bottom fraction (lane 6), indicating that palmitoylation is essential for NCAM140 to be present in lipid rafts and in the cytoskeletal-associated fraction. The blots of the NCAM140 and NCAM140Δ gradient fractions were reprobed with fyn antibodies to confirm both equal protein loading and equal isolation of the lipid raft fractions. (C) Immunoblot analysis of the total cell lysate of NCAM140- and NCAM140Δ-transfected CHO cells using polyclonal NCAM antibodies. Comparison of expression levels in CHO cells transfected with both constructs indicate that mutation of the four cysteines did not significantly alter protein expression. (D) Immunoblot analysis of the Triton X-100–soluble (S) and the Triton X-100–insoluble fraction (IS) of a CHO cell lysate using a FGF receptor-1 antibody revealed that the FGF receptor (FGFR-1) is only present in the Triton X-100–soluble fraction. IB, immunoblot for the molecules indicated.