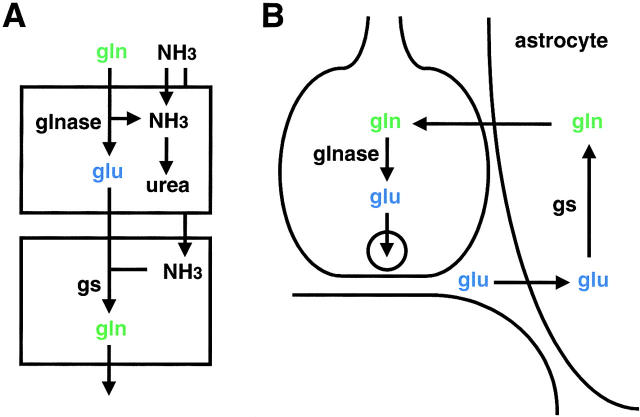
Figure 1.
The glutamine–glutamate cycles in the liver and nervous system. (A) In periportal cells (top) of the liver, glutaminase (glnase) converts glutamine to glutamate and ammonia. Along with the ammonia directly supplied from the portal circulation, the ammonia derived from glutamine feeds into the urea cycle. The glutamine synthetase (gs) in perivenous cells (bottom) converts the ammonia that escapes the urea cycle into glutamine. (B) In the nervous system, the glutamate released by exocytosis from nerve terminals is taken up by astrocytes through known excitatory amino acid transporters and converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase. Glutamine is then transferred from astrocytes to neurons and converted back to glutamate by glutaminase before packaging into vesicles.