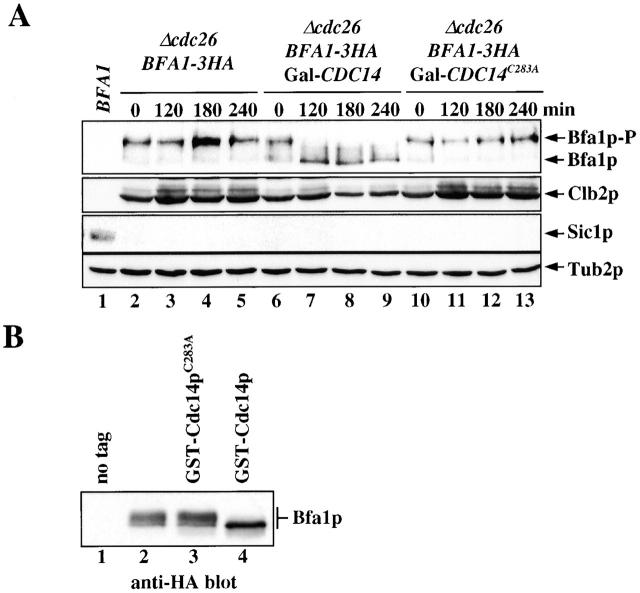
Figure 3.
Cdc14p dephosphorylated Bfa1p. (A) Cdc14p dephosphorylates Bfa1p in vivo. α-Factor–synchronized Δcdc26 BFA1–3HA (lanes 2–5), Δcdc26 BFA1–3HA Gal1–CDC14 (lanes 6–9), and Δcdc26 BFA1–3HA Gal1–CDC14 C283A cells (lanes 10–13) in YP raffinose medium were incubated for 2 h at 37°C. Galactose was then added to induce the Gal1 promoter (t = 0). Samples were withdrawn as indicated and analyzed for Bfa1p phosphorylation, Clb2p, and Sic1p by immunoblotting. The anti-Tub2p immunoblot was used as a loading control. BFA1 cells (lane 1) in G1 were used as a negative control for anti-HA and as a positive control for anti-Sic1p antibodies. (B) Cdc14p dephosphorylates Bfa1p in vitro. cdc15-1 (lane 1) and cdc15-1 BFA1–3HA (lanes 2–4) cells were grown for 3 h at 37°C until >95% arrested in anaphase. Cell extracts were incubated with anti-HA antibodies coupled to protein G–Sepharose to precipitate Bfa1p–3HA (Pereira et al., 2000). Immunoprecipitations were incubated with buffer (lanes 1 and 2) or with purified GST–Cdc14pC283A (lane 3) or GST–Cdc14p (lane 4) for 1 h at 37°C as previously described (Jaspersen and Morgan, 2000). Proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibodies.