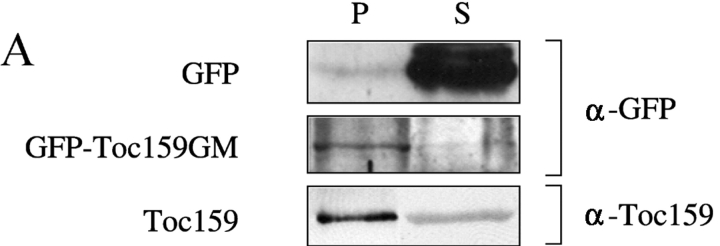
Figure 1.
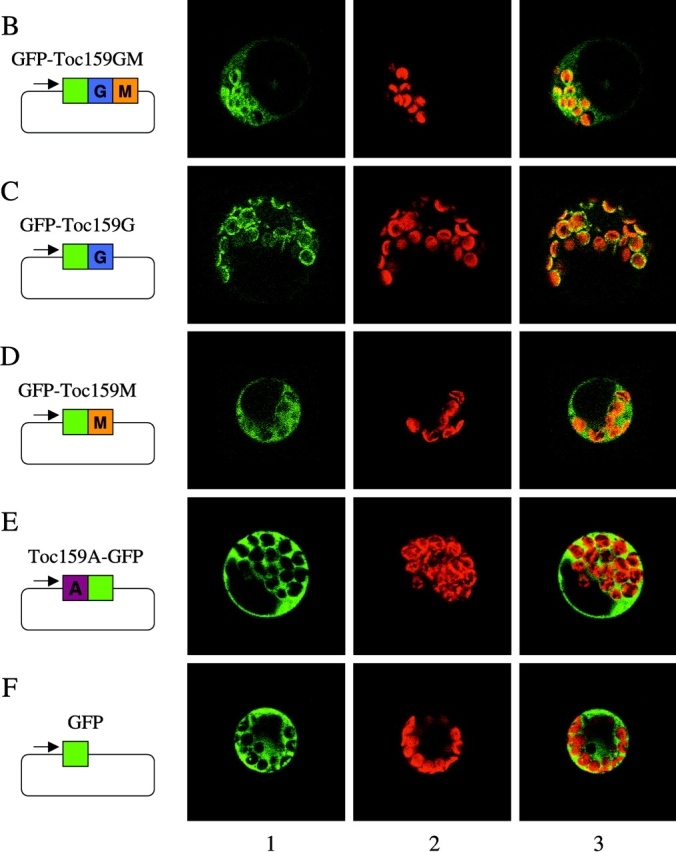
Transient expression of atToc159 domains fused to GFP. GFP fusion constructs were transformed into isolated Arabidopsis protoplasts using the PEG method. Expression of GFP fusion proteins was monitored by Western blotting to confirm functionality of a GFP fusion to the NH2 terminus of the G- and M-domains of atToc159 (Fig. 1 A; GFP-Toc159GM) or confocal laser scanning microscopy using a Leica DM IRBE microscope and a Leica TCS SP laser (Fig. 1, B–F). (A) Western blotting of the carbonate-extracted total membrane fraction (P) and soluble fraction (S) of protoplasts expressing either GFP or GFP-Toc159GM. Proteins were detected using either antibodies against GFP (α-GFP) or the A-domain of atToc159 (α-Toc159) to detect full-length endogenous atToc159. (B) GFP-Toc159GM. (C) GFP-Toc159G, NH2-terminal GFP fusion to the G-domain. (D) GFP-Toc159M, NH2-terminal GFP fusion to the M-domain. (E) Toc159A-GFP, COOH-terminal GFP fusion to the A-domain. (F) GFP control. Lane 1, GFP fluorescence; lane 2, autofluorescence; lane 3, merge of GFP and autofluorescence.