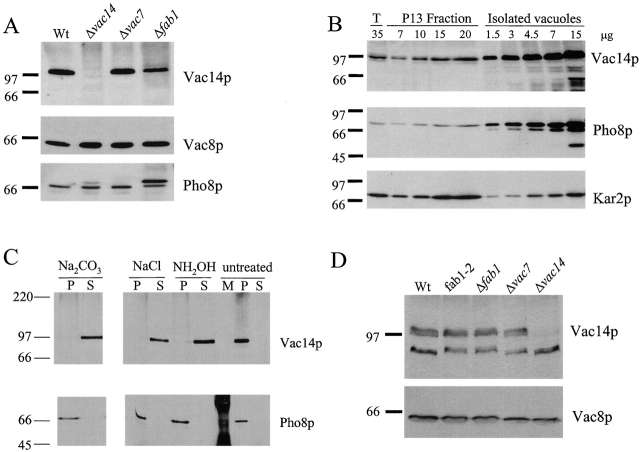
Figure 4.
Vac14p is peripherally associated with isolated vacuoles. (A) Vacuoles from wild-type, vac14-Δ1, vac7-Δ1, and fab1-Δ1 were isolated on Ficoll flotation gradients. Equivalent protein amounts were loaded in each lane. Western blot analysis was performed with anti-Vac14 and anti-Vac8p antibodies. The nitrocellulose blot was then reprobed with anti-Pho8p antibodies at a 1:1,000 dilution. (B) Vacuoles were isolated from LWY7235. 35 μg of the total cell extract (lane 2) and increasing amounts of the P13 fraction (lanes 3–7), as well as increasing amounts of vacuoles (lanes 8–13), were loaded onto a 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Western blot analyses were performed using polyclonal anti-Vac14p, anti-Pho8p, and anti-Kar2p antibodies. (C) Vacuoles were prepared, divided into six equal aliquots, and treated on ice with one of the following conditions: 0.1 M Na2CO3, pH 11.5, 1 M NaCl, 0.8 M NH2OH, or left untreated. Samples were centrifuged at 100,000 g for 1 h at 4°C. The resultant supernatant fractions (S100) were separated and the pellets (P100) were resuspended in 100 μl cytosol cocktail. Equal amounts of each were separated on a 7.5% SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with anti-Vac14 antibody. The nitrocellulose blots were then reprobed with monoclonal anti-Pho8p antibodies. (D) Equal amounts of protein from total cell extracts were loaded into each lane of a 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The proteins were then transferred to nitrocellulose. Western blot analyses were performed using anti-Vac14 antibodies and anti-Vac8p antibodies.