Figure 1.
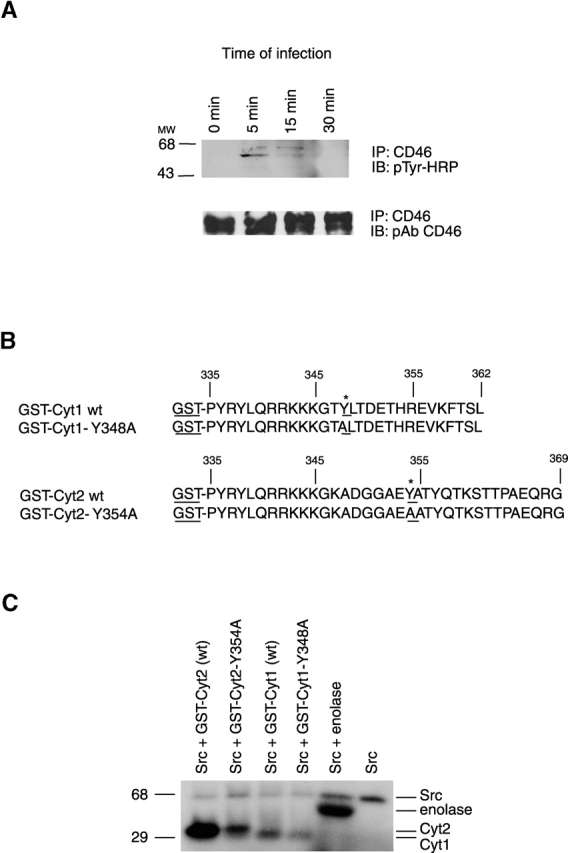
Identification of the site of CD46 tyrosine phosphorylation. (A) Presence of phosphotyrosine in CD46 immunoprecipitated from GC-infected cells. CD46 was immunoprecipated from A431 cells infected with MS11 N400 for various lengths of time using an anti-CD46 monoclonal antibody (Immunotech). The presence of phosphorylated tyrosine residues in the precipitate (top) was determined by immunoblotting with HRP-labeled monoclonal antibodies to phosphotyrosine (pTyr-HRP). Total levels of CD46 in the precipitates (bottom) were determined by reprobing the same blot with polyclonal antibodies (pAb) to CD46 (a gift from J. Atkinson, Washington University). (B) Sequences of the CD46 tails fused to GST. The Cyt1 and Cyt2 isoforms of the CD46 tail were fused to GST at Pro-335. In the GST-Cyt1 Y348A fusion protein, tyrosine at position 348 was changed to alanine. In the GST-Cyt2 Y354A fusion, tyrosine at position 354 was changed to alanine. (C) Phosphorylation of GST-Cyt2 by c-Src. GST fusion proteins were incubated with exogenous c-Src (Upstate Biotechnology) and [γ-32P]ATP in an in vitro kinase assay with enolase (Sigma-Aldrich) as the control substrate for Src activity.
