Figure 8.
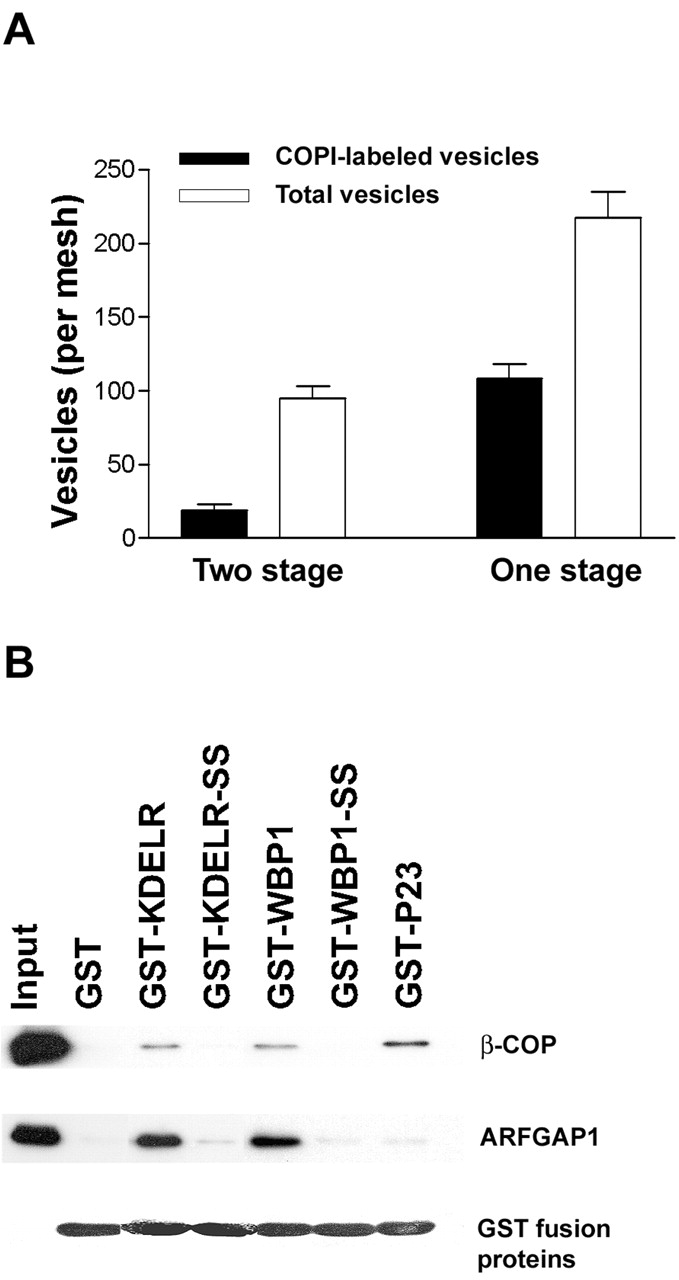
Functional evidence that GAP acts as a component of the COPI coat. (A) Simultaneous recruitment of GAP and COPI is more efficient for vesicle formation than separating the two into distinct incubation steps. A one-stage incubation was performed by incubating Golgi membrane with ARF1, coatomer, and GAP in the presence of GTP for 10 min. The level of vesicles, total or COPI labeled, from this incubation was compared with that from the standard two-stage incubation using the same amount of Golgi membrane and purified components, where the second stage was performed for 10 min. (B) GAP interacts directly with the cytoplasmic domain of COPI cargo proteins in a dilysine-dependent manner. GST fusion proteins that contain different cytoplasmic domains of cargo proteins were gathered onto glutathione-bound beads followed by incubation with either purified coatomer or GAP. Beads were washed and then analyzed by immunoblotting to assess COPI and GAP or by Coomassie blue staining to assess the level of GST fusion proteins on beads.
