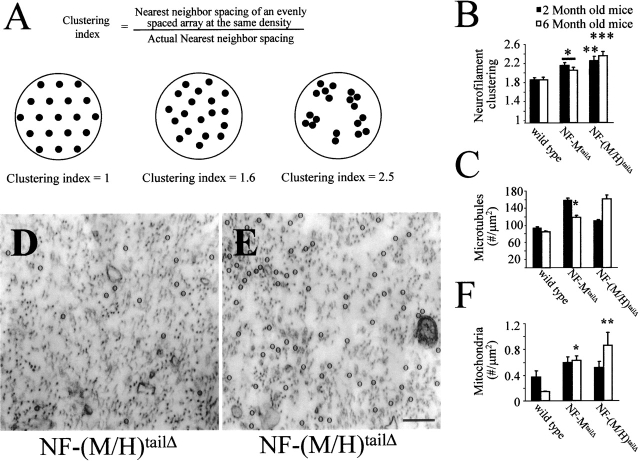
Figure 4.
Neurofilament tail domains are required for organizing axoplasm. (A) Neurofilaments (black dots) in cross sections of ideal, wild-type, and NF-(M/H)tailΔ axons were rearranged to form an array of regular hexagons encompassing the equivalent cross-sectional area. Note that the number of neurofilaments in all conditions is equal, however, the average distance each neurofilament is shifted to form triangle vertices is much greater for the tailless axon. (B) Neurofilament clustering, defined as the ratio of average filament spacing to nearest neighbor spacing, was significantly higher in both NF-MtailΔ and NF-(M/H)tailΔ mice at both 2 and 6 mo, indicating less axoplasmic organization in mice expressing truncated neurofilaments. Clustering was analyzed for overall statistical analysis using ANOVA with subsequent Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison post-hoc analysis for pairwise comparisons. *, P < 0.05 NF-MtailΔ versus wild type at 2 and 6 mo; **, P < 0.01 NF-(M/H)tailΔ versus wild type at 2 mo; ***, P < 0.001 NF-(M/H)tailΔ versus wild type at 6 mo. (C–E) Microtubule content was reflective of overall axoplasmic disorganization. A trend toward accumulating more microtubules occurred in both NF-MtailΔ and NF-(M/H)tailΔ mice (C) but did not reach statistical significance. (D and E) Electron micrographs from two different axons of the same L5 motor root from a single NF-(M/H)tailΔ mouse highlights the heterogeneity of microtubule accumulation that results from loss of both NF-M and NF-H tail domains. Bar, 200 nm. Microtubule content was analyzed for overall statistical significance using ANOVA with subsequent Bonferroni multiple comparison post-hoc analysis for pairwise comparisons. *, P < 0.05 NF-MtailΔ versus wild type. (F) Mitochondria accumulate in regions of high axoplasmic disorganization. At 6 mo, in both NF-MtailΔ and NF-(M/H)tailΔ mice, vesicle accumulation was significantly higher than age-matched controls (F). Vesicle accumulation was analyzed for statistical significance using Mann-Whitney test. *, P < 0.008 NF-MtailΔ versus wild type; **, P < 0.05 NF-(M/H)tailΔ versus wild type.