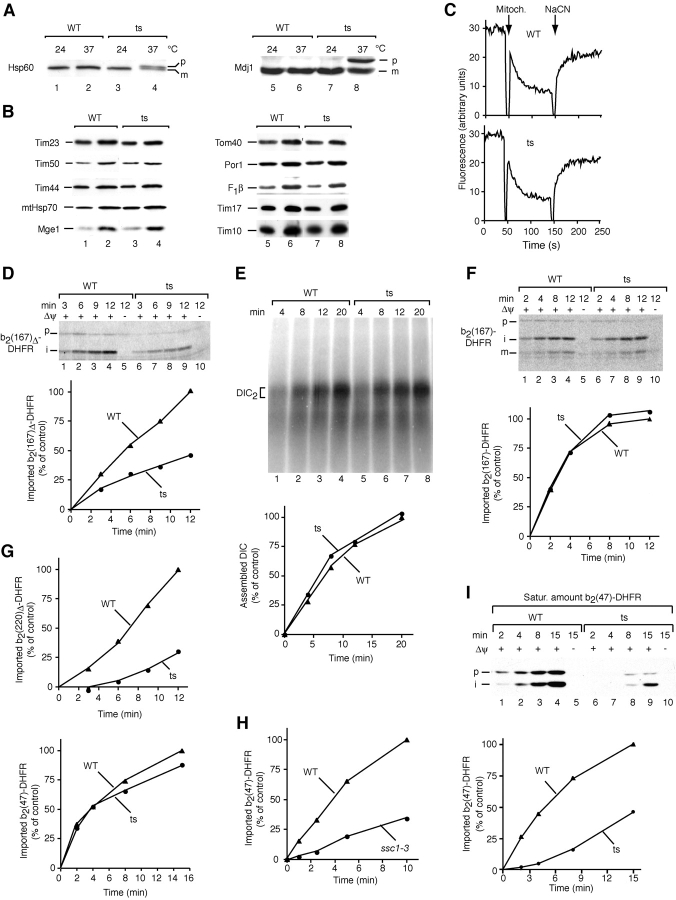
Figure 3.
The essential mitochondrial J-protein is selectively required for import of matrix proteins. (A) Accumulation of the precursors of mitochondrial proteins in J mutant cells (pam18–1; ts) shifted to 37°C for 16 h. (B) Protein levels. Isolated mitochondria (15-μg protein, odd-numbered lanes; 30-μg protein, even-numbered lanes) were analyzed by Western blotting. Nonrelevant gel lanes were excised digitally. (C) J mutant mitochondria (ts) generate a Δψ. The Δψ was assessed by fluorescence quenching using the dye DiSC3(5). (D) Impaired import of a matrix protein. 35S-labeled precursor was imported into mitochondria. Samples were treated with proteinase K and analyzed by digital autoradiography. (E) Import of a carrier protein is not affected. Dicarboxylate carrier (DIC) import and assembly into its dimeric form were analyzed by blue native PAGE and digital autoradiography. (F) Sorting of cytochrome b 2 at the inner membrane is not inhibited in J mutant mitochondria. Import of radiolabeled precursor was performed as described for D. (G) A relation of the J dependence on preprotein length. Radiolabeled precursors were imported as described above. (H) Import of b2(47)-DHFR is inhibited in ssc1–3 mitochondria. (I) J mutant mitochondria are impaired in import of saturating amounts of b2(47)-DHFR. Urea denaturated purified precursor was imported for the indicated times. Samples were treated with proteinase K and analyzed by Western blotting. The quantification shown is the average of at least three independent experiments. Import into wild-type mitochondria after the longest incubation time was set to 100% (control). p, precursor; i, intermediate; m, mature.