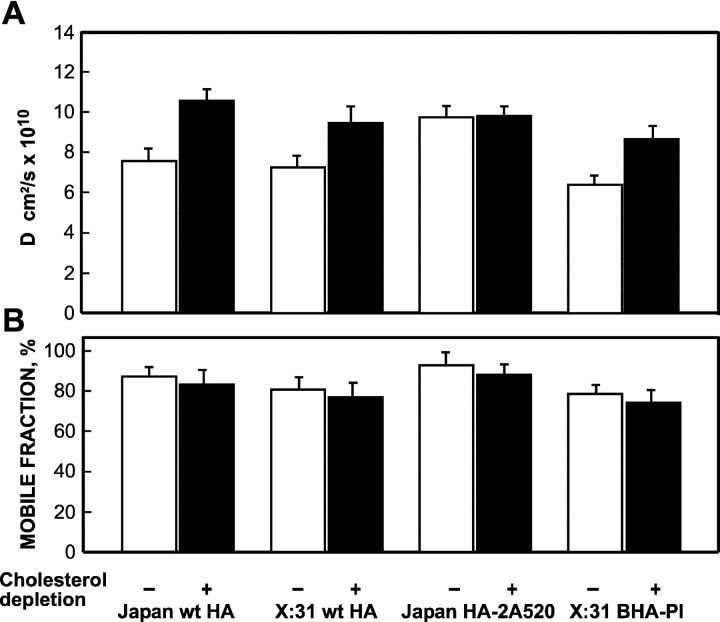
Figure 3.
Cholesterol depletion elevates the lateral diffusion rates of DRM-associated HAs to the level of the nonraft HA-2A520. The experiments were performed as in Fig. 2, on CV-1 cells infected with recombinant SV40 virions (36 h after infection) or transiently transfected with the relevant SV40 expression vectors encoding each HA mutant (48 h after transfection). Analogous experiments were conducted on COS-7 cells transiently transfected with the same vectors (24 h after transfection). In all cases, these incubation periods include 18–20-h cholesterol depletion treatment where applicable. Similar results were obtained on both cell types. Cell surface HAs were labeled with monovalent Fab' (100 μg/ml α-Japan TRITC-Fab' for Japan HAs, or 50 μg/ml α-X:31 rabbit Fab' followed by 50 μg/ml GαR TRITC-Fab' for X:31 HAs). Each bar is the mean ± SEM of 30–40 measurements. (A) D values. D of Japan HA-2A520 on untreated cells was significantly higher than D of wt HA (Japan or X:31) or of X:31 BHA-PI (P < 0.001). The effects of cholesterol depletion on the D values of the wt HAs (P < 0.001) and X:31 BHA-PI (P < 0.01) were significant; D of Japan HA-2A520 was not significantly affected by this treatment (P > 0.25). (B) Mobile fraction (R f) values. There were no significant differences between the R f values of Japan wt HA and Japan HA-2A520 (P > 0.1), or between X:31 wt HA and X:31 BHA-PI (P > 0.25). The R f values were slightly reduced after cholesterol depletion, but this effect was not significant in all cases (P > 0.05) and was observed also for the Japan HA-2A520 mutant.